Imagine you have a fantastic shop, but it’s hidden in a place where no one can find it. That’s a bit like having a website not optimized for search engines.
On-page SEO is the key to changing that and ensuring your website is the main attraction on the internet.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or just a beginner, this post is designed to provide you with a solid understanding of on-page SEO techniques and how they can benefit your website.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have all the knowledge you need to optimize your web pages effectively and improve your search engine rankings.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started.
1 What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, is like the star quality that makes your website shine on the internet stage. 🌟
It’s about making your site both search engine and user-friendly.
On-page SEO includes all the techniques applied directly to a webpage to secure a prominent place on a Search Engine Results Page (SERP). However, it’s not just about achieving a high ranking; it’s about doing so effectively.
This is achieved through a strategic blend of content and technical elements to elevate a page’s overall quality. In other words, the more you fine-tune your on-page SEO, the more traffic you’ll attract to your website, and the better that traffic will align with your content.
Optimizing a webpage with on-page SEO involves numerous aspects, which we’ll discuss shortly. These optimizations serve to enhance your page’s ranking and include:
- Improving content quality to engage and inform visitors effectively.
- Fine-tuning technical on-page elements that make your webpage more accessible and appealing to search engines and users.
In a nutshell, on-page SEO involves fine-tuning your website’s visible and behind-the-scenes parts to enhance its search engine ranking and attract fresh traffic.
2 Importance of On-Page SEO
On-page SEO helps search engines like Google find your website easily. Like signs help people find the exact way, on-page SEO helps search engines find your website.
Users who search for their queries online usually click on the first few results. A study by Sistrix found that the first organic result in Google Search enjoys an impressive average click-through rate of 28.5%. In comparison, the second and third positions receive a substantial 15% and 11% click-through rate, respectively.
On-page SEO helps your website reach the top, meaning more users will visit your site.
3 How to Perform On-Page SEO
Now that you’ve understood on-page SEO, it’s important to understand that it’s not just about getting users to your site; it’s about keeping them there.
So, let’s discuss how you can perform on-page SEO and reach the top of the search engines.
3.1 Keyword Research
Keyword research is a foundational practice in the world of Search Engine Optimization (SEO). It involves identifying and analyzing the specific words and phrases users use when searching online.
While performing keyword research, it’s important to consider the intent behind each keyword.
Are users looking for information, products, or local services?
Tailor your content to match the user’s intent. For instance, “How to groom a poodle” is informational, while “Buy a poodle grooming kit” is transactional.
Start by brainstorming potential keywords relevant to your website, products, or services. These can be single words (short-tail keywords) or longer phrases (long-tail keywords).
Short-tail keywords are brief and usually consist of one or two words. They’re often broad and cover general topics. For example, “shoes” or “travel.”
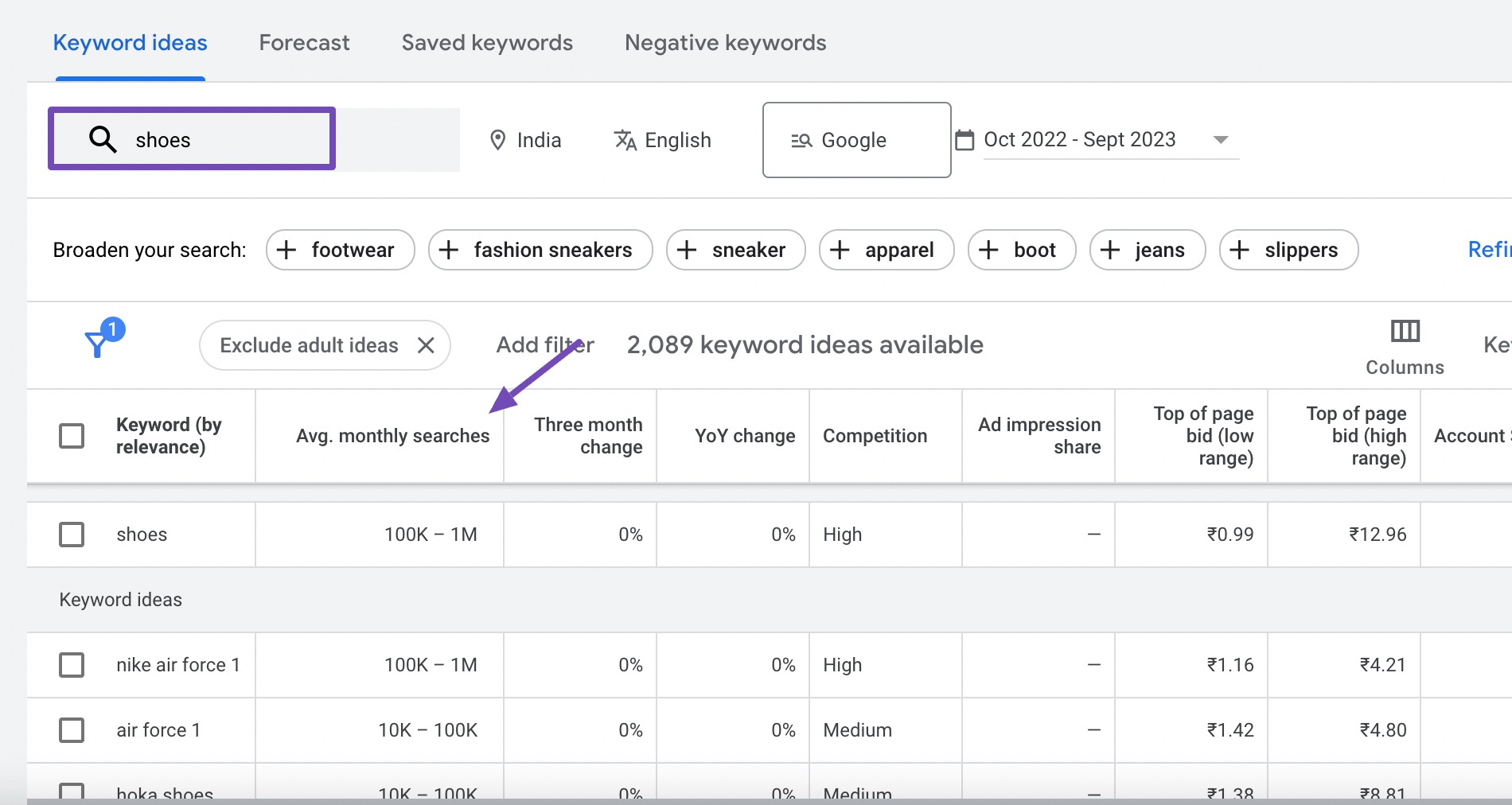
Long-tail keywords are more extended phrases, specific, and provide more context. For instance, “running shoes for flat feet” or “best budget-friendly travel destinations in Italy.”
Suppose you have a website selling running shoes. Using a short-tail keyword like “shoes” may attract a vast audience, but not necessarily the right one. On the other hand, optimizing for the long-tail keyword “best running shoes for flat feet” will likely bring in users seeking exactly what you offer, leading to higher conversion rates.
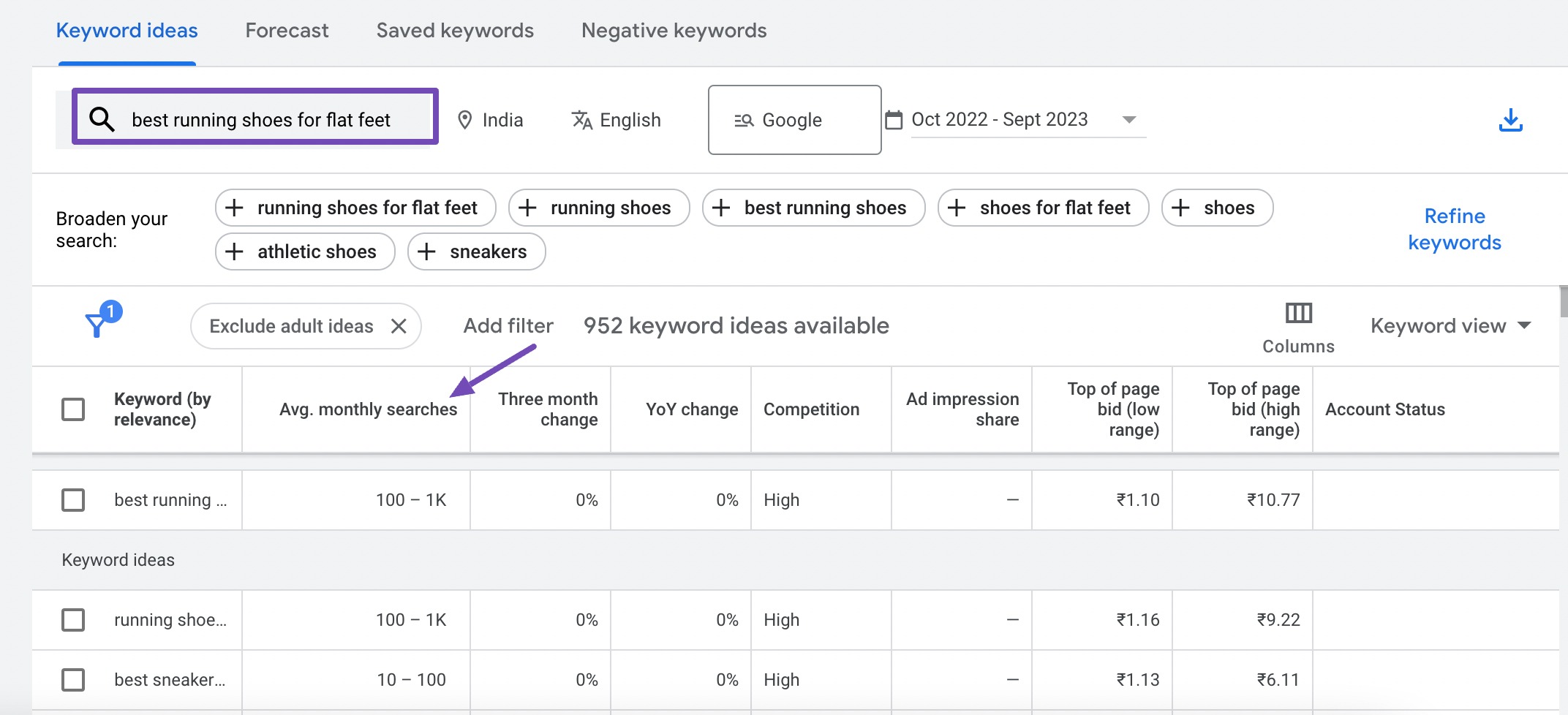
Evaluate the competitiveness of keywords. Highly competitive keywords are harder to rank for, especially for new websites. Focus on a mix of less competitive and moderately competitive keywords. For instance, “Pet supplies online” is highly competitive, but “organic dog food brands” have moderate competition.
Use keyword research tools and platforms like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to expand your list of potential keywords. These tools provide data on keyword search volume, competition, and related terms.

Rank Math makes it extremely simple to perform keyword research. Rank Math’s integration with the Google Trends tool (available in Rank Math PRO) allows you to examine keyword search trends and make comparisons.
You can also gain valuable insights into your competitor’s SEO strategies using Rank Math’s SEO Analyzer.
Finally, create high-quality, informative, engaging content around your chosen keywords. This content should answer user queries, solve problems, or provide valuable information.
You can further refer to our video, which will help you perform keyword research with actionable steps.

Quick Actionable Tips for Keyword Research:
- Understand User Intent: Start by comprehending the intent behind the keywords – whether users are seeking information, products, or local services.
- Prioritize Long-Tail Keywords: Focus on long-tail keywords, which are more specific and often have lower competition, offering a better chance to rank.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze your competitors’ keyword strategies to identify gaps, opportunities, and emerging trends.
- Utilize Keyword Research Tools: Use keyword research tools to discover valuable keywords and gather data on search volume and competition.
- Regularly Update and Refine: Keyword research is an ongoing process. Continually monitor and update your strategy based on performance and evolving trends in your industry.
3.2 Content Quality
To rank well in search results and engage your audience, your content must be of high quality and provide value. This means it should be informative, well-written, and relevant to your target audience.
Google’s content policies prioritize creating people-first content to ensure a positive user experience and uphold the integrity of the search results.

To optimize your content, you need to strategically place these keywords throughout your text, including in titles, headings, and the body of your content.
For instance, if you’re writing a blog post about camping gear, you can naturally incorporate relevant keywords like “best camping tents” or “camping equipment reviews” within the content.
But note keyword stuffing is discouraged and can negatively impact content quality.
Search engines favor original content. Duplicate or copied content can lead to lower rankings. Hence, your content should be unique and distinctive.
Quick Actionable Tips for Content Quality:
- Thorough Research: Conduct in-depth research on your topic to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your content.
- Engaging Writing: Create engaging, well-structured, and easy-to-read content.
- Quality Over Quantity: Prioritize quality over word count. Focus on delivering value and answering your audience’s questions effectively.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Do not stuff keywords unnecessarily in your content.
3.3 Use Title Tags and Heading Tags
Title and heading tags are essential elements in on-page SEO, helping structure and optimize your web content for search engines and users.
Title Tags
Search engines give title tags significant importance and are typically displayed as clickable links in search results. Therefore, including your target keyword in the title tag is crucial for better search visibility.
Title tags often serve as your audiences’ first interaction with your brand in search results. Hence, creating compelling and consistent title tags contributes to brand recognition and trust.
Clear and relevant title tags enhance the user experience by previewing the page’s content. Your audience is more likely to click on a result with a title that aligns with their search intent.
Heading Tags (H2, H3, etc.)
The H1 tag defines a web page’s primary title. They serve as the headline that gives users and search engines a clear idea of the page’s topic.
For instance, if your web page is about “10 Tips for Healthy Eating,” the title tag (H1) should be something like:
10 Tips for Healthy Eating
Heading tags (H2, H3, and so on) are used to structure the content on your page. They break down the main topics into subtopics, making your content more organized and scannable for readers.
In the “10 Tips for Healthy Eating” article, you might use H2 tags for each tip:
Tip 1: Start with a Balanced Breakfast
,
Tip 2: Include a Variety of Fruits and Vegetables
, and so on.
To identify pages lacking H1 tags, conduct a site audit using Rank Math’s SEO Analyzer. Alternatively, if you don’t have Rank Math installed on your website, you can access Rank Math’s SEO Analyzer here.
Quick Actionable Tips for Title Tags and Heading Tags:
- Use Descriptive Titles: Craft titles that convey the main topic or purpose of the page, making it easy for both audience and search engines to understand.
- Incorporate Keywords: Include relevant keywords naturally in your titles and headings to improve SEO and match user search intent.
- Hierarchy Matters: Use a hierarchical structure for headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to organize content logically and improve readability.
- Avoid Duplicating Titles: Each page should have a unique title to prevent confusion and improve search engine indexing.
3.4 Write Compelling Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are concise snippets of text that provide a brief summary of a web page’s content. They appear in search engine results and are crucial in attracting clicks and engaging users.
Google recommends that you fill in your meta descriptions and not leave them blank.

Keep your meta description under 160 characters to ensure it displays completely on search results. Be clear and concise in describing the content of your page.
Integrate relevant keywords into your meta description, especially the primary keyword for the page. Rank Math checks whether you’ve included the focus keyword in your meta description. If not, you’ll see the “Add Focus Keyword to your SEO Meta Description” error.

You must also convey the value users will gain by visiting your page. Address their needs or problems, and suggest that your page provides the answers or solutions they seek.
You can use our SEO Description tool to create compelling meta descriptions automatically. You can refer to our article on how to add SEO Meta Titles, Descriptions, and Focus Keywords in Rank Math.
Quick Actionable Tips for Compelling Meta Descriptions:
- Be Concise and Relevant: Craft concise meta descriptions under 160 characters that directly relate to the content on the page and entice the audience to click.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA): Encourage your audience to take a specific action by including a persuasive CTA in your meta description, such as “Learn more,” “Discover,” or “Get started.”
- Incorporate Target Keywords: Include relevant target keywords naturally in your meta description.
3.5 Optimize Your URLs
Optimizing your URLs is a crucial aspect of on-page SEO, contributing to improved search engine rankings and a better user experience.
Google recommends incorporating relevant words within your page URLs, and a straightforward approach is to include your target keyword in the URL slug.
URLs should be clear, concise, and descriptive of the page’s content. Avoid long URLs that are difficult to read or understand. For instance, instead of "www.example.com/category/page1234?var=132&ref=456," use "www.example.com/healthy-smoothie-recipes."
Incorporate relevant keywords into your URLs, especially the primary keyword for the page. This helps search engines understand the page’s content and can improve search rankings.
Like meta descriptions, Rank Math also checks the availability of the primary focus keyword in your URL.
If the focus keyword is present in the URL, Rank Math will show a green checkmark, indicating that it’s well-optimized. If the keyword is missing from the URL, it will display a red “X,” suggesting that you should consider editing the URL to include the keyword.
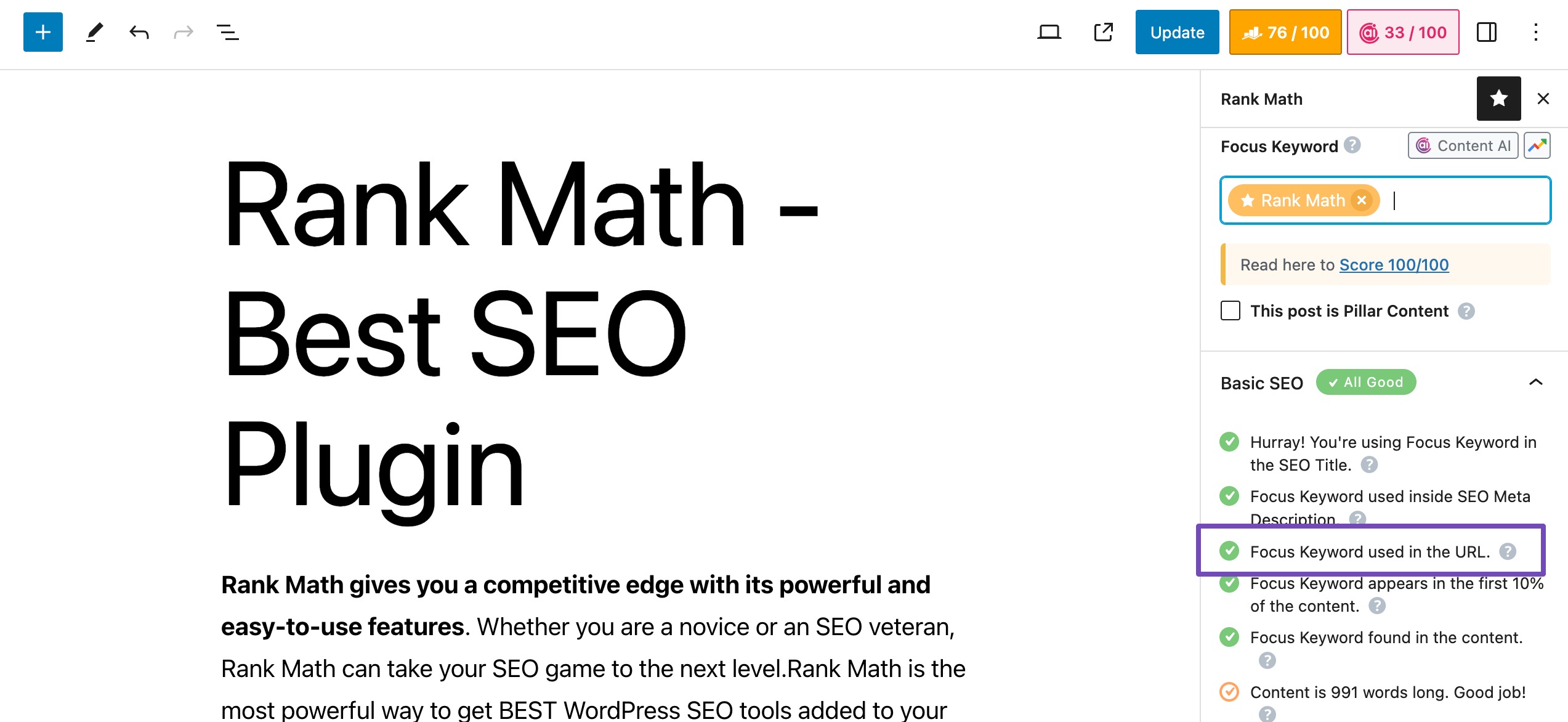
By using Rank Math’s test for focus keyword availability in the URL, you can improve your on-page SEO and increase the chances of your content ranking higher in search engine results for the chosen keyword. It’s a valuable tool for optimizing your WordPress content for better search visibility.
Quick Actionable Tips for Optimizing URLs:
- Keep URLs Descriptive: Craft URLs that clearly reflect the content and topic of the page, making it easy for both users and search engines to understand.
- Incorporate Relevant Keywords: Include relevant keywords in the URL to enhance search engine optimization. Place them near the beginning for better visibility.
- Avoid Special Characters: Use hyphens (-) to separate words in URLs, avoiding special characters, underscores, or spaces for readability and SEO-friendliness.
- Short and Simple: Create short and straightforward URLs that are easy to remember and share.
3.6 Image Optimization
Image optimization is a vital on-page SEO practice that involves two key elements: alt text for images and managing image file sizes and formats.
Alt text, or alternative text, is a concise, descriptive attribute assigned to images. It serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it ensures accessibility by providing text descriptions for visually impaired users or those with image-loading disabilities.
Secondly, it aids SEO by helping search engines comprehend the image’s content. Adding proper and descriptive alt text helps the images to appear in the search results, thereby driving more traffic to your site.

The size and format of images directly impact website performance. Large image files can slow page loading, leading to poor user experiences and lower search engine rankings.
Additionally, choosing the right image format for the type of image and the desired balance between quality and size (e.g., JPEG for photos and PNG for images with transparency) ensures smoother page loading and better SEO performance.
Quick Actionable Tips for Optimizing Images:
- Image Compression: Reduce image file sizes using compression tools to enhance website loading speed and user experience.
- Descriptive File Names: Rename image files with meaningful keywords to improve SEO and help search engines understand the image content.
- Alt Text: Always include descriptive alt text to provide context for the visually impaired audiences and enhance accessibility.
- Use Appropriate Formats: Choose the right image format (JPEG for photos, PNG for transparency).
3.7 Use Internal Linking
Internal links play a pivotal role in enhancing user navigation and engagement. They guide the users on your website to relevant content, reduce bounce rates, and encourage longer on-site visits.
Anchor text, the clickable text within a hyperlink, is an important internal linking element. Optimizing anchor text involves using descriptive, keyword-rich phrases that give users a clear idea of the linked content.
It improves user experience and helps search engines identify the topic of the linked page. Not only this, but the balanced, natural use of anchor text also reinforces the relevance and authority of your pages.

Rank Math has a feature that can mark a piece of content as Pillar Content. When you label a piece of content as Pillar Content, you’re signaling to Rank Math that this content is evergreen, and it empowers Rank Math to create meaningful internal links to connect with these specific pages or posts.
Rank Math checks your post in real time and informs you if your post does not have any internal links. You can then add an internal link and improve the on-page SEO of your post/page.
Quick Actionable Tips for Internal Linking:
- Relevance is Key: Link to related content within your website to provide users with additional, relevant information.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Create anchor text that clearly describes the linked content to improve user experience and SEO.
- Avoid Overlinking: Don’t overdo it – focus on providing value, and avoid excessive internal linking, which can be distracting or seen as spammy.
- Regularly Update Links: As your content evolves, update and maintain internal links to keep them current and functional.
3.8 Use External Linking
External linking involves strategically embedding hyperlinks that direct users to other websites in your web content.
External links boost your content’s credibility by providing supporting evidence and references. When you link to reputable and authoritative sources, you signal to your audience that your content is well-researched and trustworthy.
For instance, in an article about health, citing medical journals or institutions like the World Health Organization as external references boosts the credibility of your information.

From an SEO perspective, while the primary purpose of external links is not to boost rankings, they can indirectly contribute.
Search engines take note of the quality and relevance of external links, which can impact the perceived authority of your content. Linking to respected sources within your niche enhances your content’s relevance, potentially improving its visibility in search results.

Like internal links, Rank Math checks if you’re linking to a few external websites. If you’re not, you’ll fail the test and need to add relevant links to external websites to pass this test.
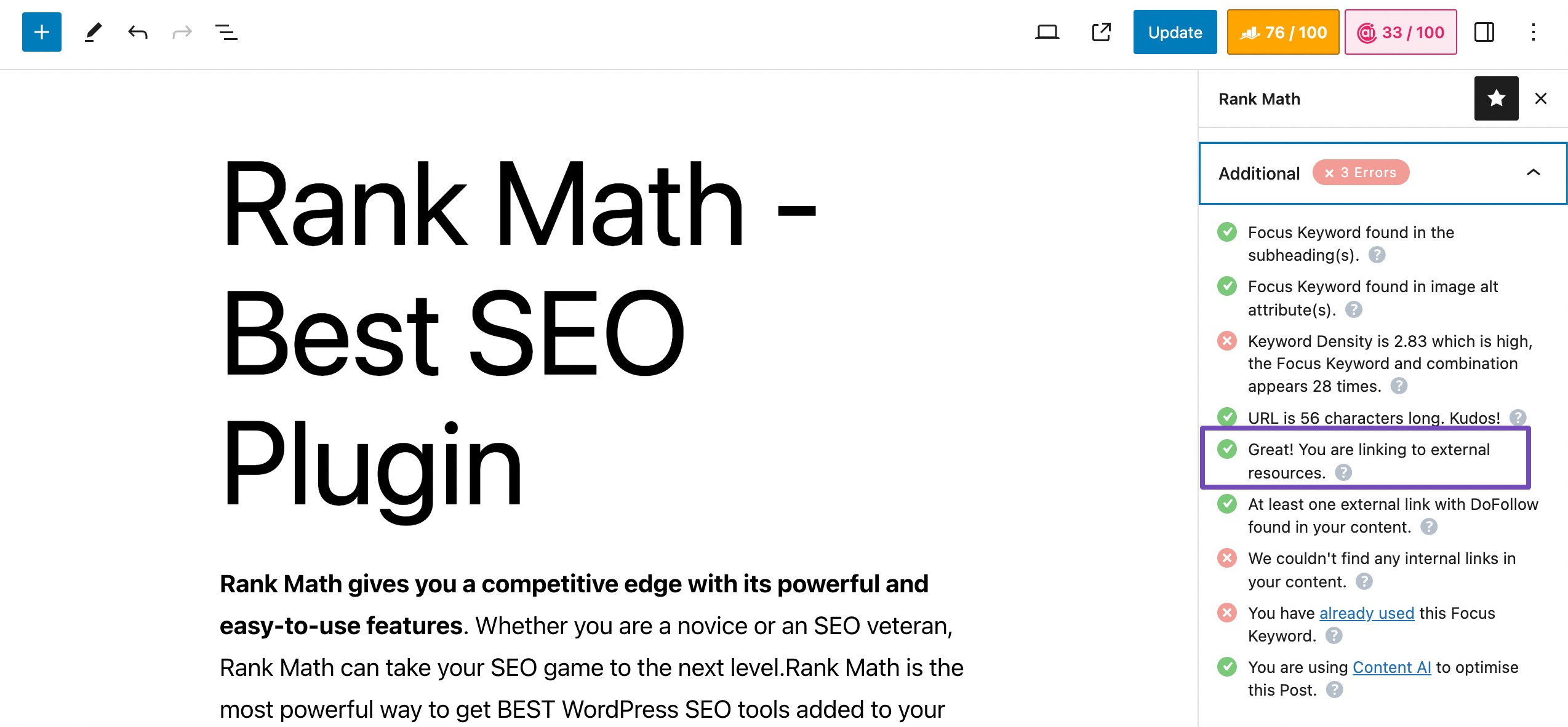
However, avoid excessive linking, prioritize relevance, ensure your linked sources are reliable, and enhance your content’s value. Striking the right balance in your external linking strategy can significantly benefit your on-page SEO efforts.
Quick Actionable Tips for External Linking:
- Authority Matters: Prioritize authoritative and trustworthy sources to boost your content’s credibility.
- No Broken Links: Regularly check and update external links to ensure they remain functional and do not lead to broken or outdated content.
4 Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between on-page SEO and off-page SEO?
On-page SEO concentrates on optimizing factors within a webpage, while off-page SEO deals with external factors. Simply put, on-page SEO involves elements entirely under your control, whereas off-page SEO involves factors beyond your control.
How can I measure the success of my on-page SEO efforts?
You can measure on-page SEO success using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Monitor organic traffic, keyword rankings, click-through rates, and user engagement metrics to assess your on-page SEO performance.
How often should I update my content for on-page SEO?
Regularly updating and refreshing content can help maintain its relevance and search engine rankings.
What is the ideal keyword density for on-page SEO?
There is no specific ideal keyword density. Focus on using keywords naturally and prioritize quality content over keyword density.
5 Conclusion
Mastering on-page SEO is essential for anyone seeking online success.
You can boost your SEO game by optimizing elements like title tags, meta descriptions, content, URLs, links, etc.
As we always say, SEO is an ongoing journey; staying updated with industry changes is important.
As you implement these strategies and continuously refine your approach, you’ll see your website climb the search engine ranks, attract more visitors, and offer real value to your audience.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.

