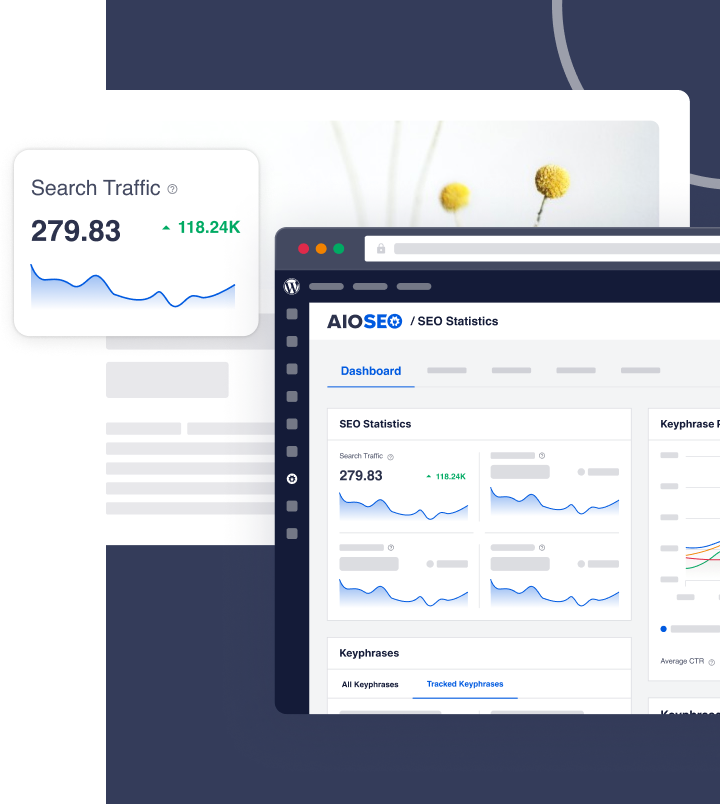
Even a simple SEO audit can lead to impressive SEO gains.
While WordPress offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of plugins to enhance functionality, it’s crucial to ensure that your WordPress site is optimized for search engines.
Conducting regular SEO audits is essential to identify areas for improvement, fix technical issues, and boost your website’s visibility in search results.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of conducting an SEO audit on your WordPress website, providing you with practical tips and tools to help you optimize your site for better search engine rankings and increased organic traffic.
Let’s start with a definition.
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a comprehensive analysis of a website’s visibility, performance, and optimization for search engines.
Conducting an audit involves examining factors that influence a website’s search engine rankings, including:
- Technical aspects: This includes site speed, mobile-friendliness, indexability, and crawlability.
- On-page elements: This covers content quality, keyword usage, meta tags, headers, and internal linking structure.
- Off-page factors: This encompasses backlink profile, business directory listings, and online reputation.
- User experience: This includes navigation, design, structure, interactivity, and overall usability of the website.
The purpose of an SEO audit is to identify opportunities for improvement in a website’s search engine optimization strategy.
What’s included in an audit can vary widely depending on the size and complexity of the website and the goals of the audit.
For instance, a local business audit should include checks of business directory listings and Google Reviews management. And a large online store will required detailed analysis of website structure and internal linking.
Many SEO audits conducted by site owners simply cover basic on-page elements.
By addressing the issues uncovered during an audit, website owners can enhance their site’s visibility, attract more organic traffic, and ultimately improve their search engine rankings.
Who Needs an SEO Audit?
Any website that relies on organic traffic for leads, sales, or brand exposure can benefit from regular SEO audits.
SEO audits are often used during transitions, like the launch of a new website or a redesign.
Problems like content not showing up in search engine results pages may also trigger an audit.
Here are some specific situations where an SEO audit is particularly important:
- Site redesigns: Before launching a redesigned website, an SEO audit can help ensure that the new design is optimized for search engines and that no important SEO elements are overlooked during the transition.
- Websites with declining traffic: If you’ve noticed a significant drop in your website’s organic traffic, an SEO audit can help identify the underlying causes and provide recommendations for improvement.
- Poor search engine rankings: If your website is struggling to rank for relevant keywords, an SEO audit can help identify the factors holding your site back and provide a roadmap for improvement.
- Competitive industries: In highly competitive industries, even minor SEO improvements can make a significant difference in search engine rankings. Regular SEO audits can help you stay ahead of the competition and maintain your online visibility.
- Local businesses: For businesses targeting a local audience, an SEO audit can help optimize your website for local search factors, such as the local Pack, Google Maps, and local keywords.
- E-commerce websites: With the growing importance of online sales, e-commerce websites need to ensure that their product pages, navigation, and checkout process are optimized for search engines and user experience.
Now, let’s get equipped with tools that will automate much of the audit process.
The 2 tools I recommend are from All in One SEO. There’s a free Chrome extension we’ll use and the AIOSEO plugin.
AIOSEO Analyzer Chrome Extension
This free SEO Chrome extension provides a convenient way to check on-page SEO basics.
You don’t need to be logged into any WordPress website to use it. It works on all sites, not just WordPress sites.
Marketing professionals can use it during discovery calls with potential clients: you can quickly identify issues that need fixing.
All in One SEO (AIOSEO) Plugin
All in One SEO (AIOSEO) is a versatile tool that enables users to conduct comprehensive on-page SEO audits and perform essential technical audits.
This is an established plugin with thousands of 5-star reviews on WordPress.org. Currently, over 3 million people are using the plugin.

Most people use AIOSEO to optimize their pages for better rankings and higher traffic.
So, you can use this tool to fix SEO issues you find during an audit.
Once you’ve installed the free AIOSEO Analyzer Chrome extension and installed the All in One SEO plugin on your site, you’re ready to audit.
How To Do an SEO Audit for WordPress
There’s no specific order of steps for an audit. Because many audits are limited to on-page SEO, we’ll start there. But feel free to reorder the steps to suit your preference.
On-Page SEO Audit
Check Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
There are 2 goals here:
- Make sure every page has a title and meta description
- Ensure these are optimized for SEO. That means checking to see that they’re precise and descriptive and that they don’t exceed recommended character lengths.
You can use the AIOSEO Analyzer Chrome extensions to check titles and descriptions.
- Navigate to a page you want to check.
- Open the extension and view the title and description information.
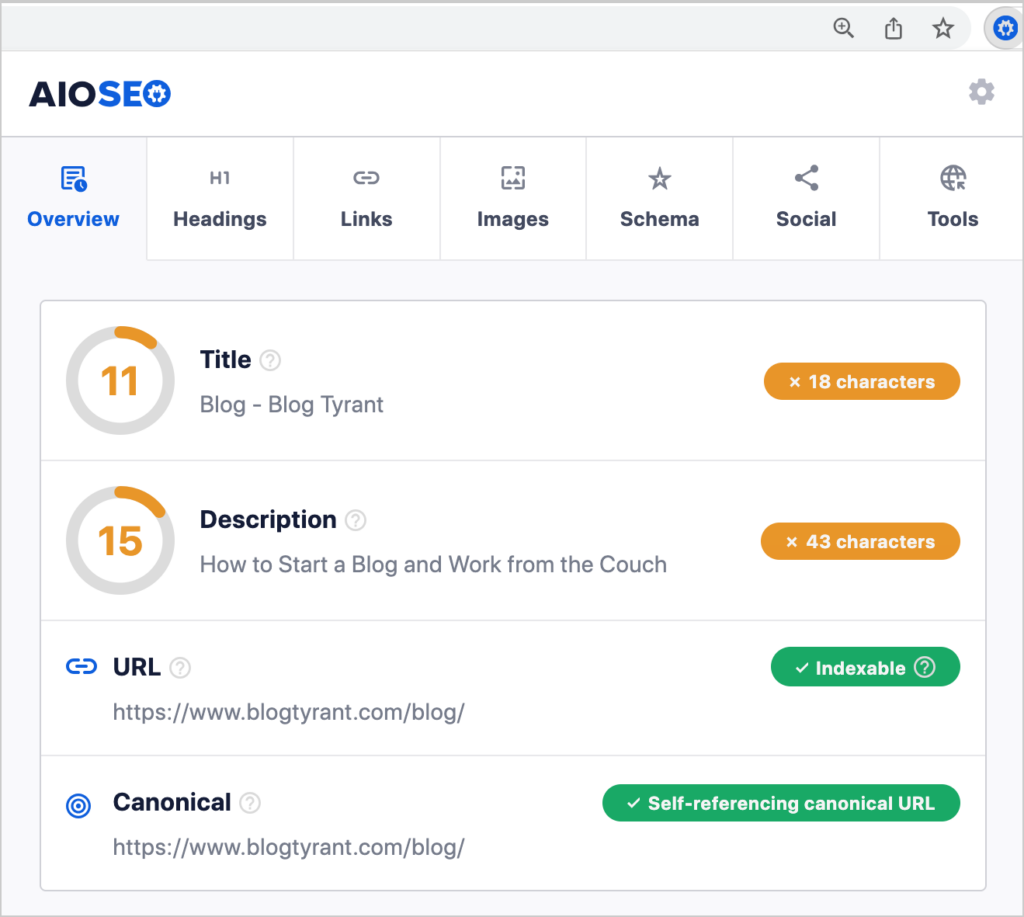

Alternatively, you can use the All in One SEO plugin for these checks. This gives you the ability to correct issues on the spot.
- To use the plugin, log into WordPress and navigate to the page to be checked.
- Click on the AIOSEO button at upper right to open the AIOSEO sidebar.
- Next, click General.
- Then, click Edit Snippet.
Now you’ll see form fields and character counts for the title tag and meta description.
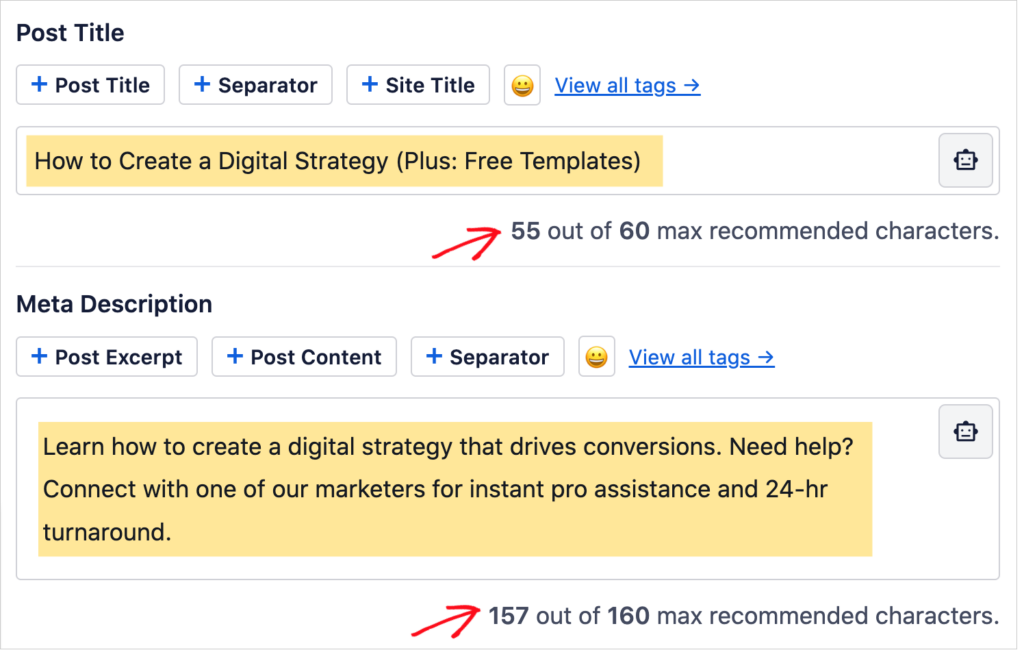

Evaluate Headings Use
Next, evaluate the use of headings on individual web pages.
What are we evaluating?
- Check to make sure there are subheadings on the page.
- Subheadings in general can help boost engagement by making content scannable.
- Using a few keyword-rich subheadings can influence rankings.
- Ensure the h-tag use makes hierarchical sense.
Use the AIOSEO Analyzer Chrome extension to do these SEO checks quickly.
- Navigate to a page to check
- Open the extension and click the Headings tab.
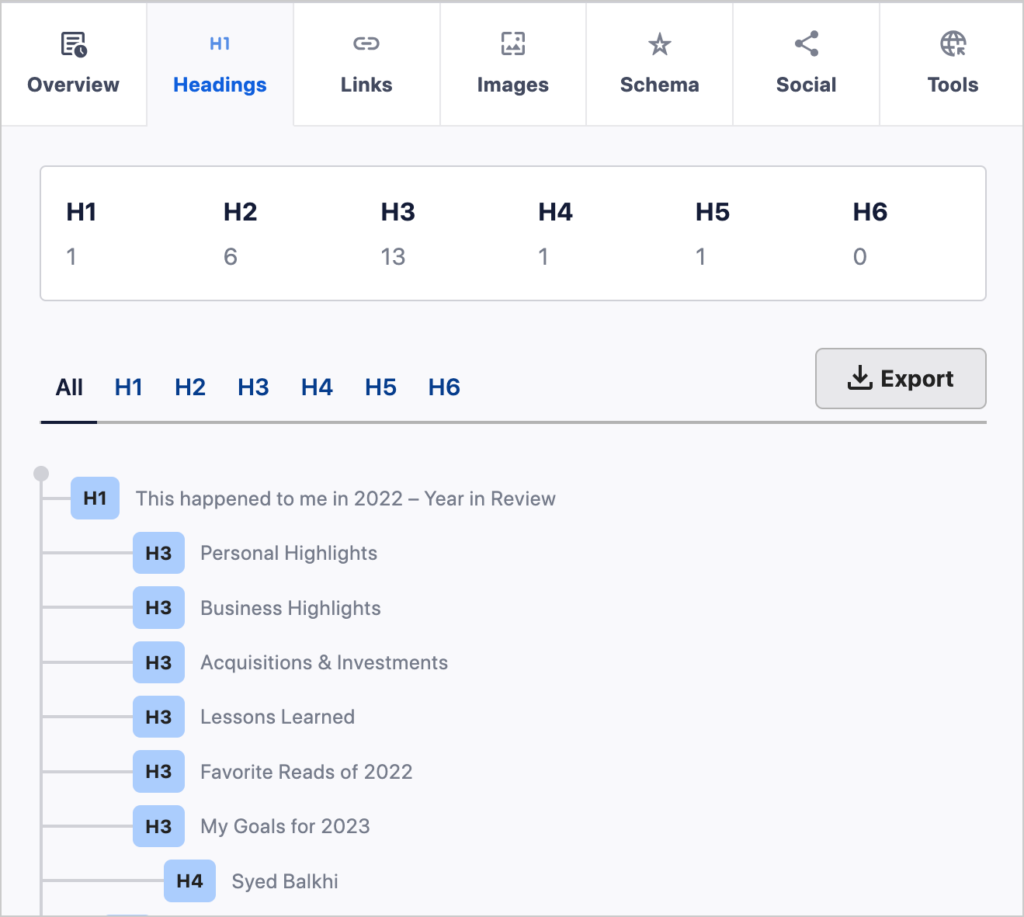

In this case we see the title has the h1 tag (which is appended automatically in WordPress). But there are no h2 tags. Instead, there are only h3 and h4 tags.
Inspect Image SEO
You can also use the AIOSEO Analyzer to check for image optimization.
Specifically, you want to check;
- Image filenames: These should be short and descriptive.
- Presence of alt text: any missing alt text should be filled in, except for decorative images. The text should be, like the filename, short and descriptive.
To do your image SEO audit:
- Navigate to a page to check
- Open the AIOSEO Analyzer extension.
- Click the Images tab in the extension.
Now you can see a list of all images that are missing alt tags.
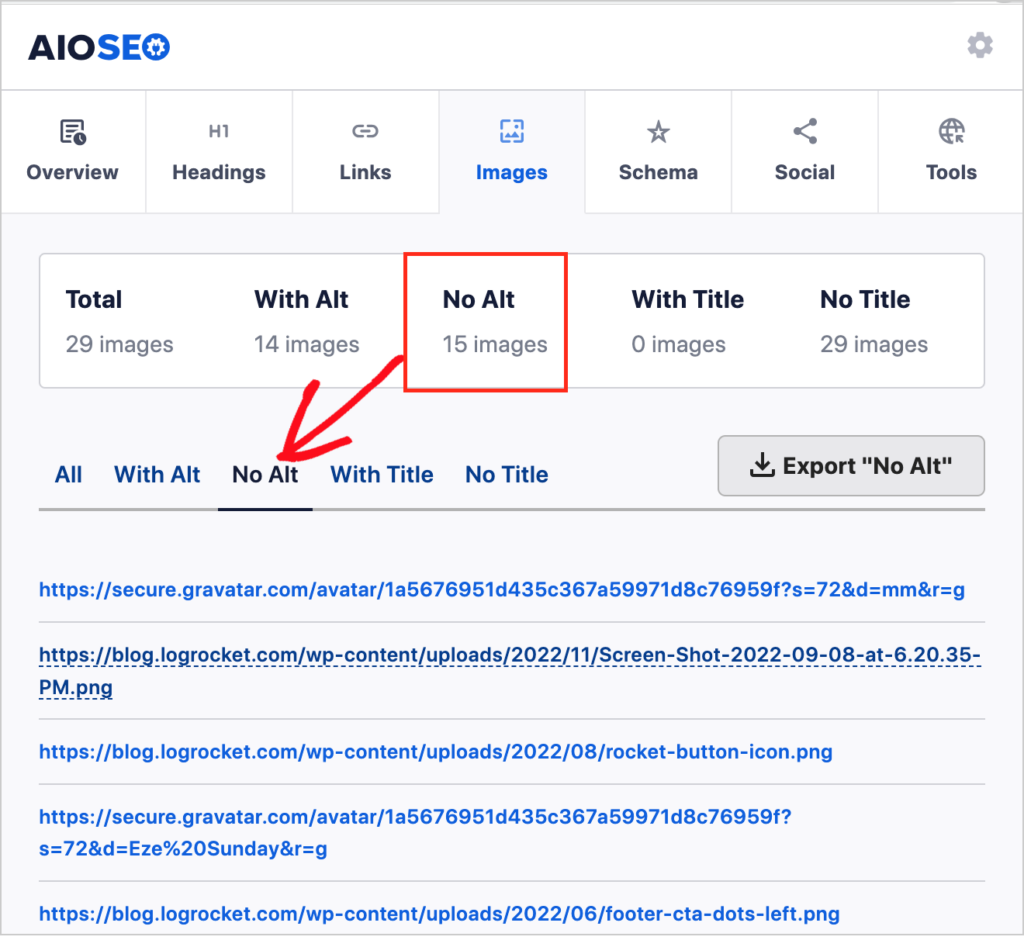

If you click on “With Alt” you’ll see the actual alt text itself.
You can also check the image filename here, but given the use of various image tools, the URLs for these image may be long. Look for the text that appears before the image file extension (e.g., before .jpg, .png, .svg)
Alternatively, you can log into the Media Library to see how well images are being named.
Here you don’t need to check every image filename. You want to simply get an idea of good practices are being followed. If they’re not, then make recommendations for optimizing image filenames.
Review Use of Internal Links
Internal links have a surprising impact on SEO. They help search engine crawlers find pages to index.
Important pages: These links also communicate a hierarchy among the site’s pages. So it’s crucial to identify your most important pages (from a business standpoint) and ensure there are plenty of internal links pointing to those pages. This linking can boost the rankings of your key pages quickly.
Examples of important pages might be your top product or service pages.
Orphan pages: Next, you’ll identify orphan pages. These are pages that have no internal inbound links.
Pillar pages: Additionally, if you’re using a topic cluster strategy, you’ll want to identify all your pillar pages.
To do your internal linking audit, I recommend you use the Pro version of the All in One SEO plugin. This version includes a Link Assistant, which will automate most of your checks.
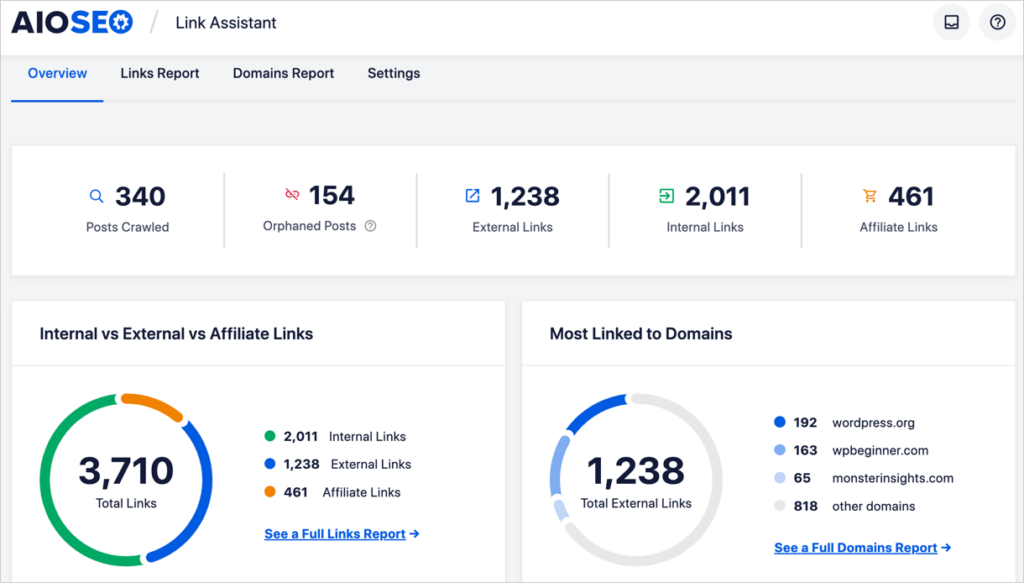

Here’s how to do your internal linking SEO audit:
- Log into WordPress and in the admin bar choose AIOSEO » Link Assistant.
- Then click on Orphaned pages. Make a note of the total number of orphaned pages.
- Next, navigate to each pillar page and each identified “important page.” Click the AIOSEO button to open the AIOSEO sidebar.
- Go to General and click Cornerstone Content
- Then toggle on the Mark as Cornerstone button.
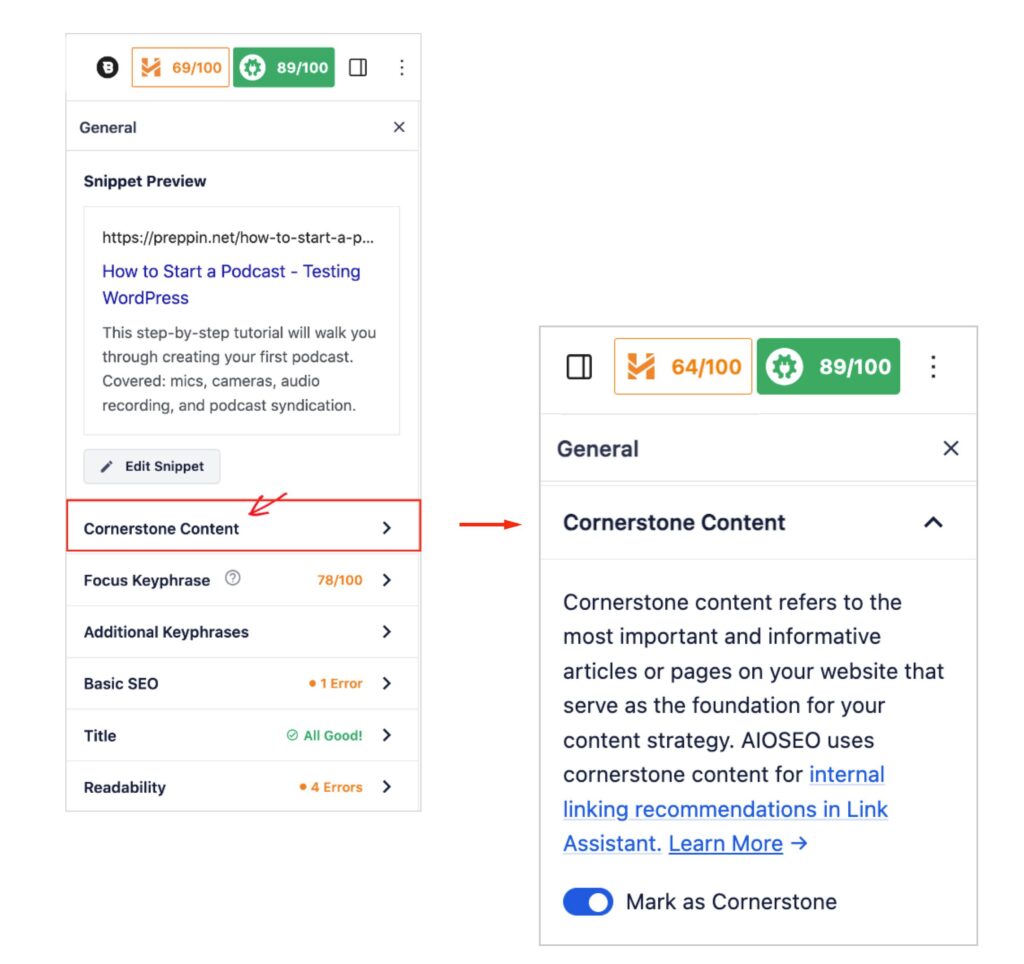

Doing this will cause the Link Assistant to prioritize link recommendations for those pages.
After you do this internal link check, you can set aside 15 minutes a day or week to build links to your orphan pages and important pages. Of these, the latter should be the priority.If you’re doing this audit for a client, then make the same recommendation to them.
With Link Assistant, you can add internal links without opening the individual pages. And you’ll get specific recommendations for those links.
Check Video SEO
If your website embeds videos in pages, then you’ll want to audit your video SEO.
- Ensure your site has a video sitemap. The Pro version of All in One SEO offers this. Follow these instructions to toggle it on.
- If you publish pages that feature 1 video only, consider adding a transcription to the page. That can help surface the video in search results.
Inspect Schema Markup
Schema markup is code that helps search engines understand your content better and rank it for relevant keywords.
With this SEO audit you’ll:
- Check pages for the presence of schema markup
- See if additional schema is warranted.
This can sound complicated but it’s rather easy.
Before you start, it’s helpful to know that All in One SEO automatically applies schema markup to:
And it’s good to know that there are different types of schema, categorized by content types, such as:
If you see an opportunity to add schema to a page with All in One SEO, all it takes is a few button clicks and you’ll fill out a form.
Now, let’s start the schema markup audit.
- Navigate to the page to be checked
- Open AIOSEO Analyzer Chrome extension
- Click on “Schema” in the extension window.
If there’s no schema present, you’ll see this:
If schema is present you’ll see this. (Pay attention only to the @type line.)
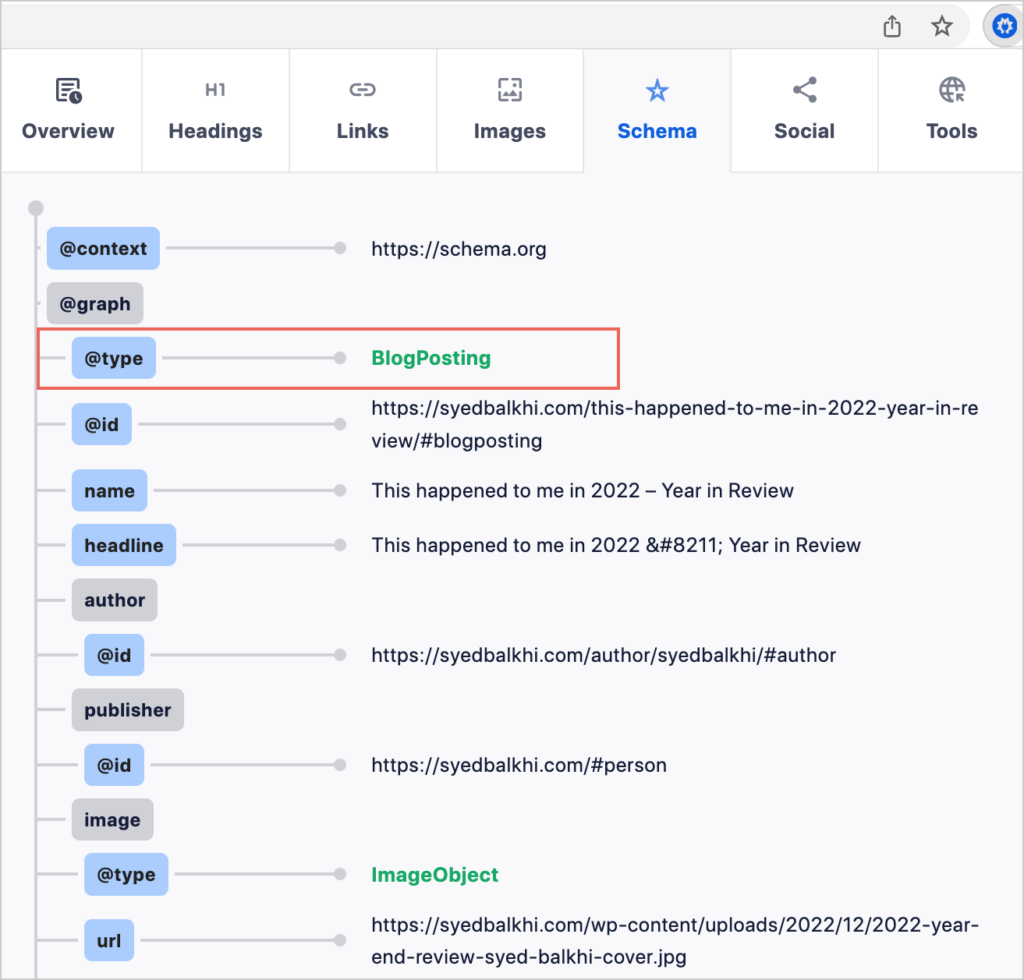

Your next step would be to make a note if the page could use additional schema.
You can add that schema at the point of the audit or later.
Now, let’s look at formatting and readability checks. These are quite easy.
Check Formatting and Readability
On every web page you can check the AIOSEO sidebar for formatting and readability recommendations.
These are found under the Readability tab.
In the AIOSEO sidebar click General, then Readability.
You’ll find an analysis of things like subheading distribution and whether images or video have been used to break up the text.


Click on an eye icon to be taken to the exact part of the page that the recommendation addresses.
In addition the plugin provides a Flesch reading ease score. General and commercial content performs better when simple language is used.


For the purposes of an audit, you’ll want to get a general idea of how well formatted pages are and what the reading scores are like.
This can inform your recommendations to a client.
Learn more in our articles on scannable content and the Flesch Reading Ease Score.
If you’re auditing your own site, you can set a goal to use the AIOSEO plugin to optimize your most important pages, and then to optimize all new content before it’s published.
This approach will help you prioritize your actions.
Next, let’s move on to check the conversion points in the website.
Conversion Point Audit
A conversion point is any interactive element designed to capture information from the user.
Common conversion points are:
- Email newsletter sign ups
- Registration forms
- Checkout pages
- Sign ups for free downloads
This audit is common sense.
Make sure:
- Everything’s working
- CTAs and key conversions are above-the-fold
- Checkouts and sign-ups are easy, not confusing
In my audits, it’s been fairly common to discover simple issues like email newsletter forms that don’t work. Typically, site owners in such situations will be complaining about a lack of leads.
In addition, broken features can cause users to distrust a website.
When you’re doing this audit, keep in mind that many users don’t bother scrolling down a page. So calls-to-action (CTAs) and conversion points should be, wherever possible, placed near the top of the page.
Keep mobile users in mind too: they have less screen space before having to scroll down.
In addition, people have become accustomed to receiving immediate email confirmations when they sign up or buy something. This provides assurance and the practice is so common that if your site doesn’t send out these emails, a user may wonder if something’s broken.
So be sure these are set up for each conversion point.
Next, let’s move on to some technical considerations.
Technical SEO Audit
You may be wondering “What’s technical SEO?” The answer is it’s defined subjectively. Typically, marketers define it as a form of SEO that deals with code or technical issues.
Some might consider simple things like schema checks as “technical SEO.”
To fully understand this subject, see our article on technical SEO audits. [link to article once it’s published.]
Here are common factors analyzed during a technical SEO audit.
Indexability
Indexability refers to the ability of search engines to discover, crawl, and index the pages of a website.
It is a crucial factor in SEO, since only indexed pages can appear in search engine results pages (SERPs). Pages that aren’t indexed miss out on organic traffic.
Here are some indexability audit checks.
Sitemaps
Your site should have both an XML and an RSS/Atom sitemap. This is keeping with Google’s recommendations.
To check for the presence of these sitemaps, in a browser. add sitemap.xml then sitemap.rss after your domain name.
Example:
Occasionally the XML sitemap may be located at a different URL, but this check usually works.
You can also use the AIOSEO Analyzer to check for the presence of an XML sitemap.
- Open the Analyzer
- In the Overview tab, scroll down to the sitemap.xml hyperlink
- Click on that hyperlink. Doing so will automatically append “sitemap.xml” to the domain you’re checking.


Good to know: WordPress generates an XML sitemap for all WP sites. However, it doesn’t generate an RSS/Atom sitemap. Here’s where the All in One SEO plugin comes in. Once you install it, it will automatically generate both an XML sitemap and an RSS/Atom sitemap.
The plugin will automatically update these sitemaps whenever you modify or publish new content. This 100% maintenance-free process is the way to go with sitemaps.
Robots.txt File and Noindex Tags
These 2 elements, when used incorrectly, can prevent web pages from appearing in search results.
Errors: So the key thing you’ll check is if there are any errors in the robots.txt file or with the use of noindex tags. You’ll do this by checking the website’s related Google Search Console account. Any errors will be listed there.
Now, let’s get clear on what the robots.txt file is and what noindex tags are. Then we’ll provide guidance on fixing related issues.
Robots.txt: A robots.txt file is a file that allows site owners to give specific instructions to web crawlers like Googlebot and Bingbot.
For instance, the file may instruct crawlers to ignore pages that the site owner doesn’t want indexed. These might be staff login pages or pages for internal use only.
However these robots.txt instructions are interpreted by crawlers as suggestions. The crawler itself will decide how it wants to handle your page. And not all crawlers interpret robots.txt file contents the same.
In addition, using the robots.txt file to “disallow” a URL won’t prevent other sites from linking to that page.
Furthermore, it’s not necessary to have a robots.txt file. It’s useful however, if you want to create custom directives. It’s also recommended if you have sitemaps. Crawlers will look at the robots.txt file to find the address for your sitemaps.
To check to see if a site has a robots.txt file, enter the domain into a browser followed by /robots.txt.
You’ll see a text file like this.
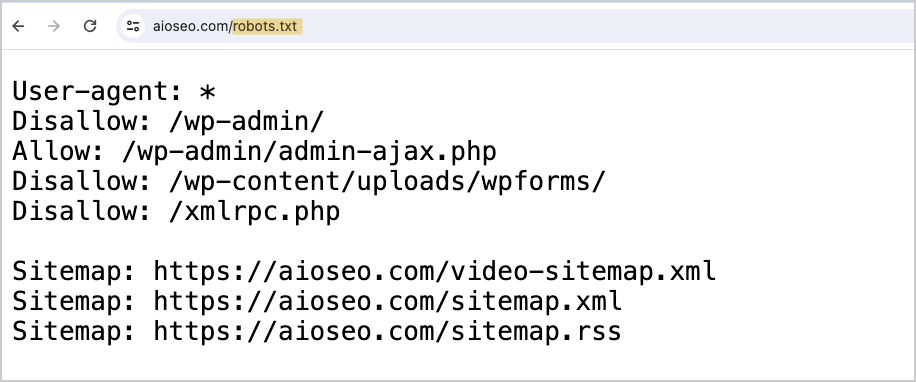

This robots.txt file is for aioseo.com. The file was automatically generated by the AIOSEO plugin. Once you install AIOSEO it will automatically generate this file, place it in the right location, and include critical information.
Here’s how to read the robots.txt file shown above.
- User agents are crawlers. These include search engine bots and specialty crawlers like those that scan websites to capture email addresses.
- Wildcard: The asterisk is a “wild card” and means “all crawlers” should pay attention to these instructions. Googlebot can understand wildcard directives, but many crawlers don’t.
- Disallowed: Pages that don’t need to be listed in search results, like WordPress login pages, are “disallowed.”
- Sitemap URLs are listed.
You can check this file to see if any content pages have inadvertently been blocked (disallowed) from search results. This can occur when an AIOSEO user customizes the robots.txt file and accidentally adds wrong information to it.
Alternatively, you can log into Google Search Console and look for any crawling or indexing errors.
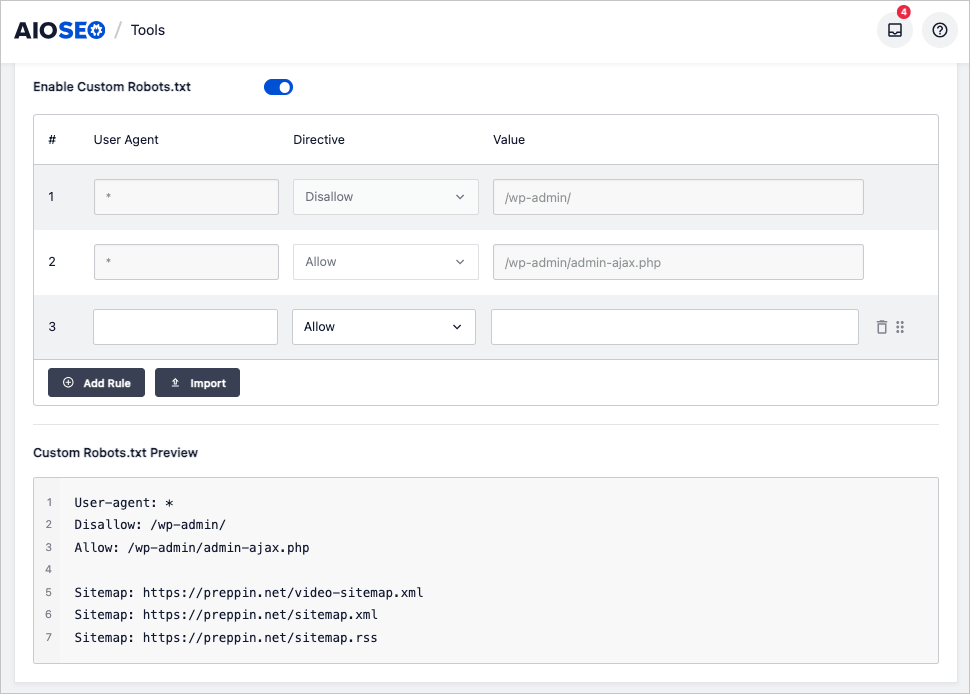

Noindex: The noindex tag can be applied to individual pages and this can also block them from being indexed. Google Search Console will tell you if there are any problems here.
The noindex tag is one of several robots meta tags.
And here, All in One SEO makes fixes easy. To remove an “noindex” tag from a page, you don’t need to touch the code.
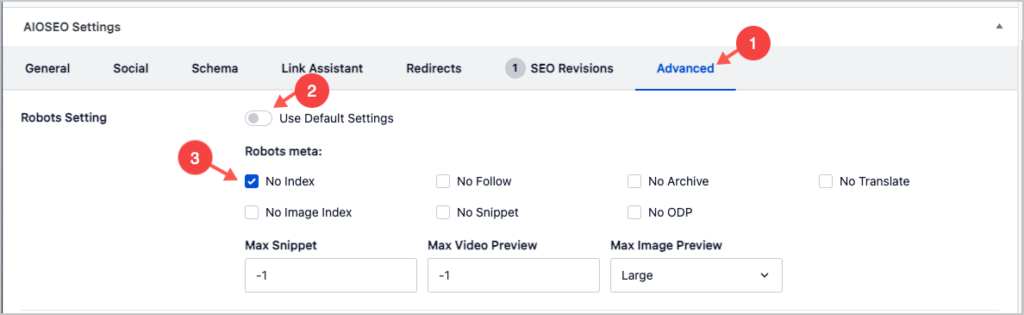
In the WordPress editor, navigate to the page that Google Search Console has an noindex tag applied to it.
- Scroll to the bottom and click on Advanced
- To the right of Robots Setting toggle off Use Default Settings
- Untick the No index checkbox.
Then save.

For more, see our video on how to use robots meta tags in WordPress.
Security
Next, you can do some basic security checks.
- HTTPS: Each site should be using HTTPS, not HTTP. Sites that use HTTP can be flagged by Chrome as “unsafe.” You’ll need an SSL certificate in order to get HTTPS security. This is usually done via your web host.
- Secure Forms: If you’re collecting visitor information you’ll want to ensure the form plugin you’re using is secure. We use WPForms but there are other reliable form plugins like Formidable Forms and Gravity Forms.
- Secure checkout: Be sure you’re using a respected 3rd-party payment gateway like Stripe or PayPal to ensure secure checkouts.
- Hacks: Check the site’s Google Search Console to ensure no hacks have occurred.
- Access Control: Not everyone on your team needs access to all WordPress features. You can use WordPress controls to curtail access.
Site Speed
Site speed can be a ranking factor although Google’s algorithms will weight quality above speed and compare your page to similar pages. So there’s a relative aspect to this.
Be aware that improving site speed is a specialized and technical field.
- Page Load Times can be tested in Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Resource Optimization: PageSpeed Insights will also give you recommendations for resource optimization. This refers to improving how code files and images load.
- Caching: Use a plugin like WP Rocket and web hosting caching to speed site loading.

WordPress users can skip the technical headaches and choose a theme designed to load fast. Options include SeedProd, Blocksy, and GeneratePress.
Mobile Factors
When you choose a new theme use your mobile phone to navigate the site. Is it easy to navigate? Are the buttons large enough for tapping?
You can easily switch themes by simply uploading a new one.
Additionally, whenever possible, place your article keyword at the beginning of each page title.
For example, if you wrote an article on the keyword “korean tacos” and this article is targeting residents of Dallas, then you might use this headline:
- Korean Tacos: 5 Killer Foodtruck Options in Downtown Dallas.
Remember: mobile search displays are narrow. Most searchers will focus on the first 2-3 words of the title.
The All in One SEO plugin will check for this specific keyword placement, and give you extra SEO “points” for this, which increases your overall score.


Site Structure
A site structure audit includes a review of the navigation (how intuitive and logical is it?) as well as how close pages are to the homepage.
Generally, it’s a good idea to try to keep pages within a few clicks from of the homepage. That makes it easier for search engines to crawl your site.
Keep in mind that the closer a page is to the homepage, the greater its perceived importance will be to search engines. So, product category pages will carry more weight than individual product pages.
Consider whether the site in question would benefit from breadcrumb navigation. If so, this can be added with the All in One SEO plugin. In addition, AIOSEO will add the related schema code for breadcrumbs, helping Google understand your site structure.

Off-Page SEO Audit
Off-page SEO may sound odd. Unlike on-page SEO, off-page SEO deals with factors that can influence your rankings but which are located on other websites.
These factors include:
- Your site’s backlink profile
- Local SEO Citations
- Brand Mentions
Check for Local SEO Citations
Google Business Profile: Small businesses and local nonprofits should create and optimize a Google Business Profile. This is essential for local rankings.
Checking a profile includes ensuring it’s fully filled out, that the correct categories have been chosen, and that the profile is routinely kept up-to-date.

Google Reviews: In addition, check to see if there’s a process for managing Google Reviews. These reviews significantly influence rankings in the local Pack and play a role in which businesses shoppers choose.
Business listings: Additionally, a small business should be listed in online directories. These directories, like Yelp and Thumbtack, often rank on page 1 of search results for local terms. Being listed can boost your businesses’ visibility and help with your local rankings overall. See how easy it is to get directory listings.

Consistent NAP: Finally, ensure the site’s NAP (short for Name, Address, Phone) is accurate and consistent across the web. NAP should be understood to include all contact info including email address(es), hours of operation, and website URL.
When you use a service like BrightLocal Citation Builder, you can sign up for a handful of data aggregators that will ensure your location is propagated to vehicle GPS systems.

SEO Audit Q&A
Are SEO audits worth it?
Yes, SEO audits can be worth it for many businesses and websites. Here are a few key reasons why:
- Identify technical issues: An SEO audit can uncover technical problems that may be hindering your website’s search engine performance, such as slow loading times, broken links, crawl errors, or duplicate content. Identifying and fixing these issues can improve your site’s visibility and rankings.
- Optimize on-page elements: SEO audits analyze on-page factors like title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and content relevance. Optimizing these elements based on the audit’s findings can make your pages more search engine-friendly and improve their chances of ranking well for target keywords.
- Assess content quality and gaps: Audits evaluate your existing content and identify areas for improvement or topics that should be covered to better target your audience’s needs and search queries. This helps you create a more comprehensive, relevant, and engaging content strategy.
- Analyze backlink profile: An audit will examine your website’s backlink profile to identify low-quality, spammy, or irrelevant links that could be hurting your rankings. It also highlights opportunities to build high-quality, relevant links to improve your site’s authority and search visibility.
- Benchmark against competitors: SEO audits often include a competitive analysis to see how your website stacks up against key competitors in terms of rankings, content, backlinks, and other factors. This provides valuable insights for refining your SEO strategy.
- Provide a roadmap for improvement: Based on the audit’s findings, you’ll receive actionable recommendations and a prioritized roadmap for improving your website’s SEO. This helps you focus your efforts and resources on the most impactful changes.
While SEO audits require an investment of time and resources, they can provide significant long-term benefits in terms of increased organic search traffic, higher rankings, and ultimately, more leads and revenue for your business.
The value of an audit depends on the complexity of your website and the competitiveness of your industry, but for most businesses, regular SEO audits are a worthwhile component of a comprehensive digital marketing strategy.
How much does an SEO audit cost?
The cost of an SEO audit can vary significantly depending on several factors, such as the size and complexity of your website, the depth of the analysis, the experience and reputation of the SEO professional or agency, and whether it’s a one-time audit or part of an ongoing SEO service package.
In this article we’ve seen how a site owner can run their own SEO audit using free and low-cost tools.
While these tools can provide valuable insights, they may not be as comprehensive or tailored to your specific needs as a professional audit conducted by an experienced SEO specialist.
Sample Price Ranges for an SEO Audit
When it comes to hiring a professional, here are some rough price ranges you might encounter:
- Basic SEO Audit (small websites, limited analysis): $500 – $2,500. At the lower end of this cost you might get an automated report that was generated in minutes by a software tool.
- Standard SEO Audit (medium-sized websites, more comprehensive analysis): $2,500 – $6,500
- Advanced SEO Audit (large, complex websites, in-depth analysis): $5,000 – $25,000+
- Hourly rates: Some SEO agencies or consultants might charge hourly rates for audits. These can range up to $500+ per hour, depending on their expertise and the scope of the work.
It’s essential to view an SEO audit as an investment rather than a cost. While the upfront expense may seem significant, the insights and recommendations provided can lead to improved search engine rankings, increased organic traffic, and ultimately, a higher return on investment for your business in the long run.
Be sure to carefully consider the scope of the audit and the qualifications of the provider when evaluating the cost and value for your specific needs.
And learn how to avoid SEO scams.
After Your SEO Audit . . .
Now that you understand SEO audits, and how you can conduct a basic one yourself, what’s next?
Read our guide to on-page SEO so that going forward you can optimize all new content pages. And if you have a local business, explore our guide to Local SEO. And don’t forget to plan for conversions.
Come join us on our YouTube Channel to find simple WordPress SEO tutorials. You can also follow us on X (Twitter), LinkedIn, or Facebook to stay in the loop.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.