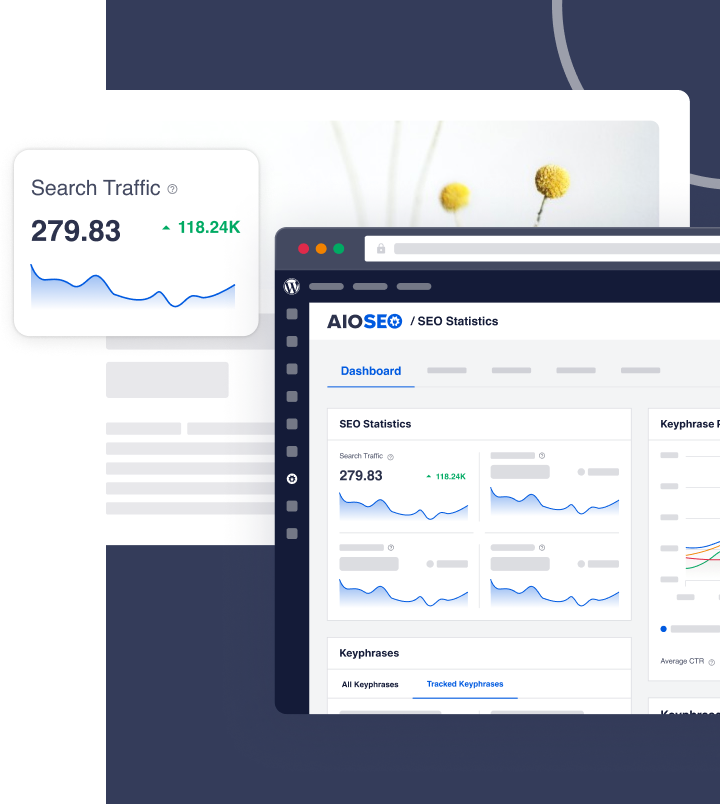
HTML sitemap vs. XML sitemap: what’s the difference?
If you’ve found yourself asking this question, you’re not alone.
Sitemaps are an essential tool for enhancing your search engine optimization (SEO) and site management. They provide a roadmap of your website’s structure, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content. However, there are two main types of sitemaps – HTML sitemaps and XML sitemaps – and they serve different purposes.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between HTML and XML sitemaps, their benefits, and which one you should use for your website.
What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that provides a structured list of your site’s pages. It’s a vital part of your technical SEO.
A sitemap is a file that provides a structured list of your site’s pages. An XML sitemap is generated to help search engine spiders like Googlebot better understand your website’s content and organization. This makes it easier for them to crawl and index the pages. An HTML sitemap, on the other hand, is for helping your readers better navigate your site.
Both formats are generally easy to generate, especially if you have a powerful WordPress SEO plugin like All In One SEO (AIOSEO).
AIOSEO is a powerful, easy-to-use SEO plugin with over 3 million active users. Because it’s regularly updated, you can rest assured the plugin stays abreast of changes in SEO best practices and keeps up with WordPress versions.
Millions of smart bloggers and marketers use AIOSEO to help them boost their search engine rankings and drive qualified organic traffic to their blogs because the plugin has many powerful features. These are designed to help you properly configure your SEO settings.
Regarding sitemaps, AIOSEO has a powerful Sitemap Generator.
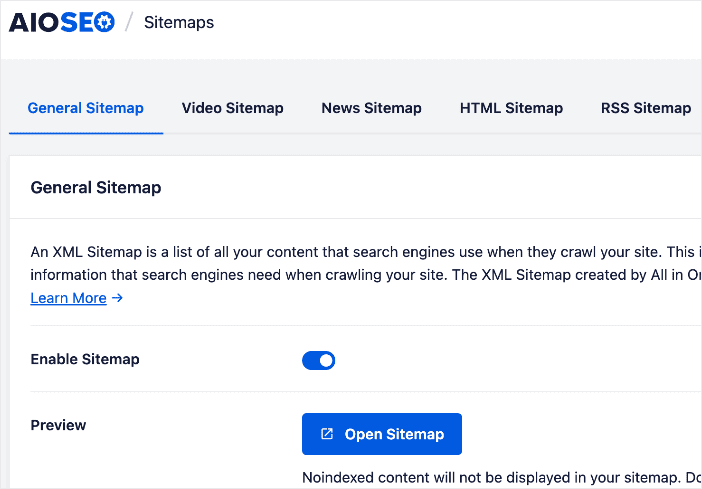
The sitemaps are easy to use, and you can customize them so that you can optimize your site for higher rankings and maximum traffic.
Besides XML and HTML sitemaps, AIOSEO also gives you the option to include video sitemaps and Google News sitemaps.
Understanding HTML Sitemaps
An HTML (hypertext markup language) sitemap is a web page listing all your site’s pages, typically in a hierarchical or alphabetical format. This helps improve site navigation for your website visitors and boosts your internal linking strategy and on-page SEO. Here’s an example of what an HTML sitemap looks like:

This type of sitemap is designed to be human-readable, meaning it helps visitors easily navigate and understand your site’s structure. Consider it a sort of table of contents to help users find relevant pages easily. This type of sitemap is especially helpful for large websites.
Benefits of HTML Sitemaps
Adding an HTML sitemap to your site has many SEO benefits, with the main ones being:
- Enhanced user experience (UX): An HTML sitemap improves the UX of your site by clearly providing a list of links to all your important pages. It helps visitors find the information they need quickly and efficiently.
- Improved navigation: HTML sitemaps can help improve the overall navigation of your site, as they provide a clear overview of the site’s structure.
- Accessibility: An HTML sitemap can offer an alternative way to find specific information for users who rely on assistive technologies like screen readers, especially if the site itself has accessibility issues.
As you can see, adding an HTML sitemap to your website is an SEO best practice to follow.
How to Generate an HML Sitemap
Generating an HTML sitemap is relatively straightforward, especially if you have an SEO plugin like AIOSEO. To start, head to your AIOSEO settings and select the Sitemaps option.
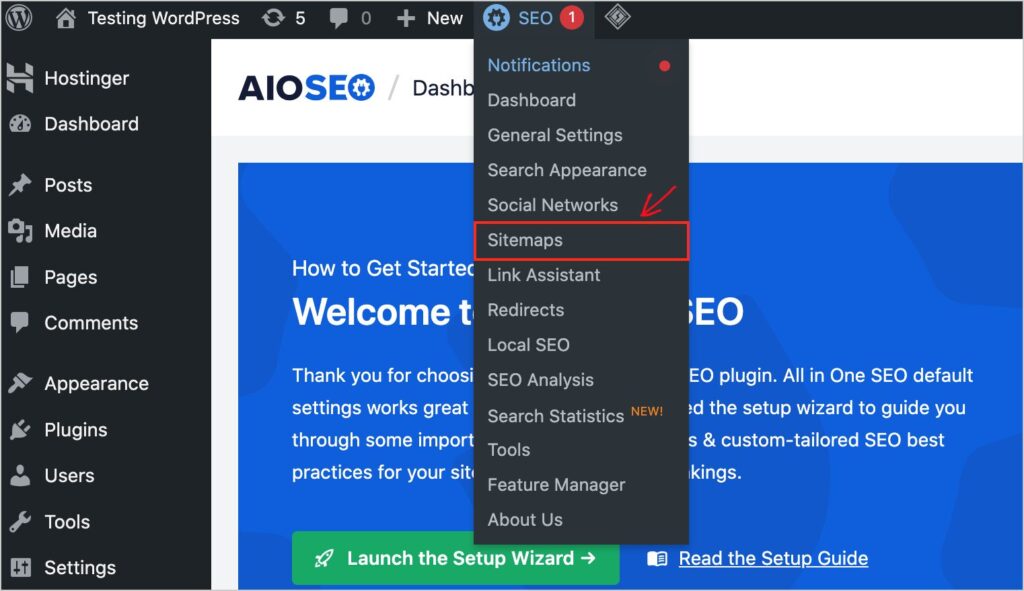
In the Sitemaps section, select HTML Sitemap and ensure the Enable Sitemap toggle is set to on.
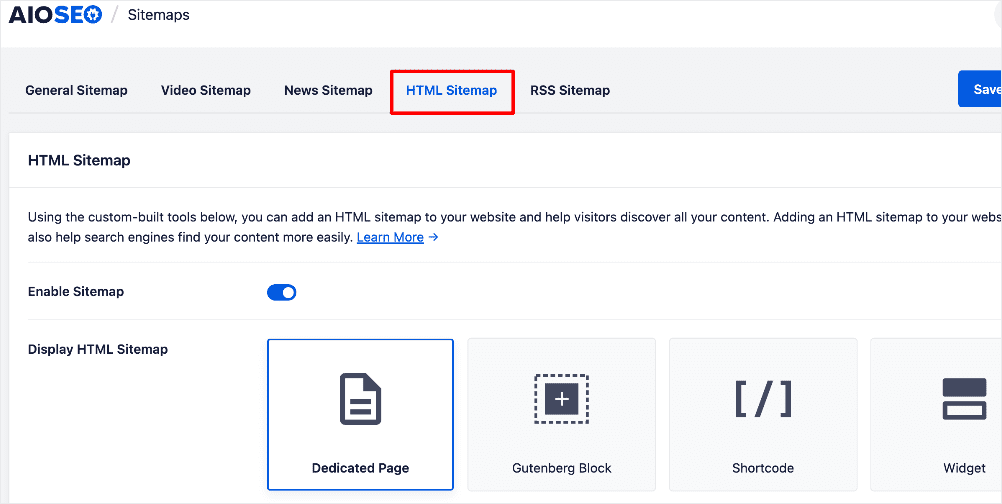
AIOSEO gives you many options for how you want to display your HTML sitemap. Options include:
The plugin also gives you advanced settings for configuring your HTML sitemap.
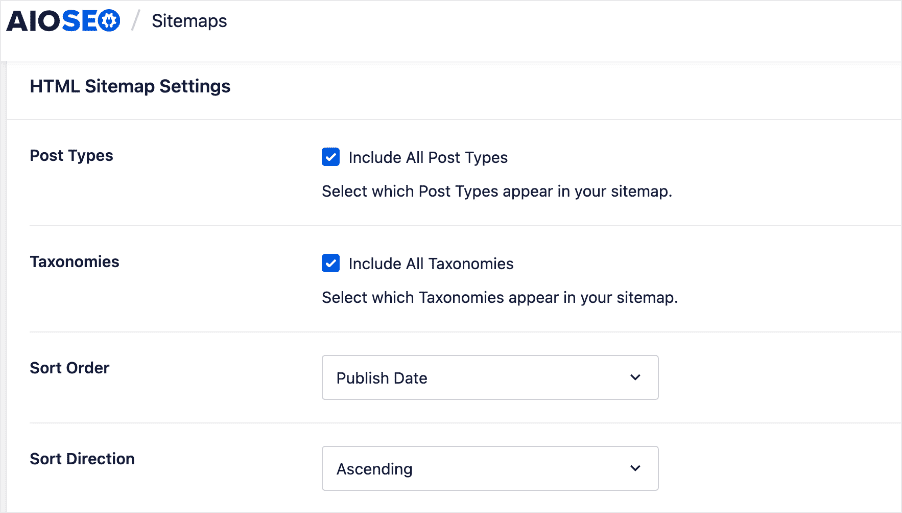
These settings give you more flexibility when customizing your HTML sitemap.
Check out our tutorial for detailed steps on generating an HTML sitemap.
Understanding XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a file listing all the important pages on your site. It also provides additional information about each page, like when it was last updated and its relative importance on your site. This is the second file web crawlers visit after the robots.txt file. As a result, it helps search engine crawlers discover your new content more easily.
XML sitemaps are written in a special format called Extensible Markup Language (XML) that search engines like Google understand. This is where they get their name from.
XML sitemaps are a sort of blueprint of your site that helps search engines discover and index all your website’s content. Submitting your sitemap to search engines makes it easier for them to crawl and understand your site, improving your website’s ranking in search results.
Here’s a simplified example of what an XML sitemap looks like:
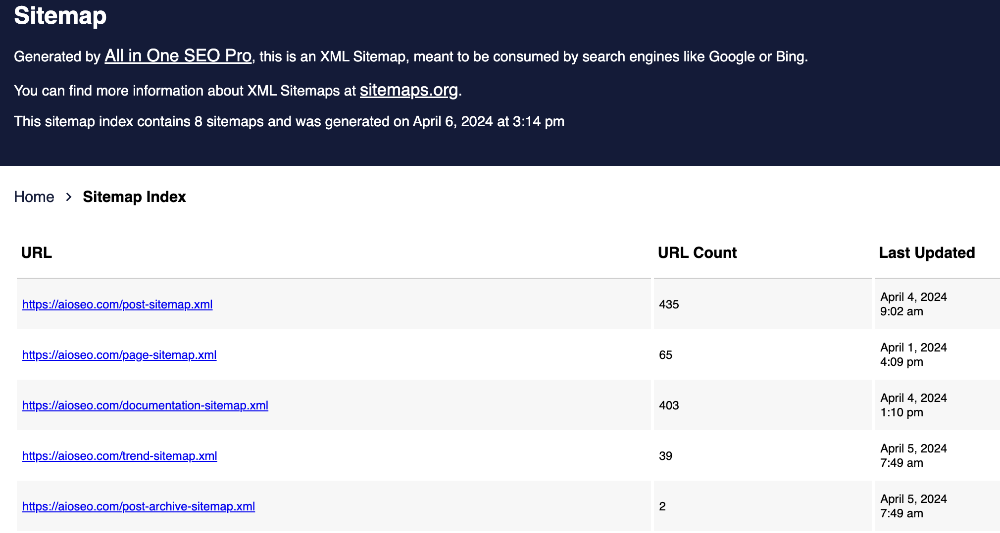
You can find your sitemap file by visiting your sitemap URL, which is: https://yoursite.com/sitemap.xml, with “yoursite.com” being your domain name.
Remember, unlike HTML sitemaps that are visually appealing, XML sitemaps are meant to facilitate communication between website owners and search engines.
The Benefits of an XML Sitemap
Creating and submitting an XML sitemap for your site offers several key benefits:
- Improved discoverability: An XML sitemap helps search engines discover and index your site’s pages more efficiently, ensuring that all your important content is easily accessible to users.
- Prioritization: XML sitemaps allow you to prioritize certain pages, such as new pages. This can help search engines understand which pages are more important and should be crawled more frequently.
- Better crawling: XML sitemaps provide search engines with a clear roadmap of your site’s structure, making it easier for them to crawl and index your pages.
- Increased search visibility: By making it easier for search engines to discover and understand your site’s content, an XML sitemap can improve search engine rankings and increase visibility for your brand. This is particularly helpful for new websites.
- Additional Metadata: XML sitemaps can include additional metadata, such as the last modification date, frequency of updates, and the importance of each page. This particularly important for the freshness ranking factor.
- Accessibility for search engines: Some sites, particularly those with a large number of pages or complex structures, may not be easily crawled by search engines. An XML sitemap helps ensure all your important pages are accessible and discoverable.
- Solve duplicate content issues: An XML sitemap can help you avoid duplicate content issues, as you can indicate in the XML file which content search engines should crawl and exclude pages they should ignore.
Generating an XML sitemap is a crucial part of a robust SEO strategy and will help boost your search rankings and drive more traffic to your site.
How to Generate an XML Sitemap
As with HTML sitemaps, generating XML sitemaps is super easy with AIOSEO’s Sitemap Generator. Simply go to your AIOSEO settings » Sitemaps » General Sitemap.

Next, make sure the Enable Sitemap toggle is set to the on position.
The XML sitemaps are easy to use, and you can customize them using the built-in settings.
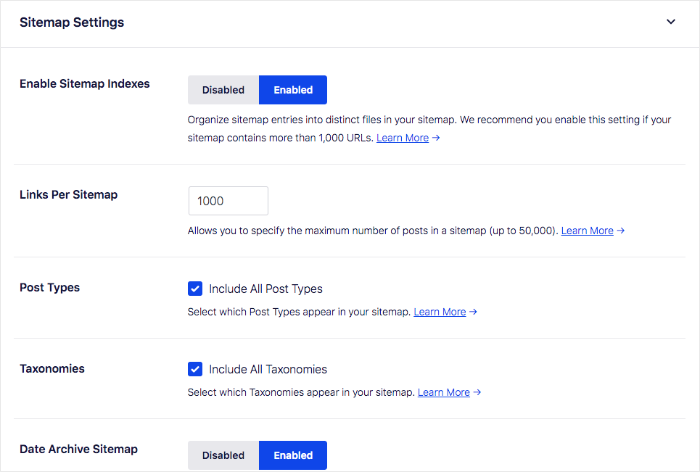
These make it easy to optimize your sitemap for efficient crawling, higher rankings, and maximum traffic.
Plus, AIOSEO’s XML Sitemap Generator gives you advanced options like uploading URLs from a CSV file.
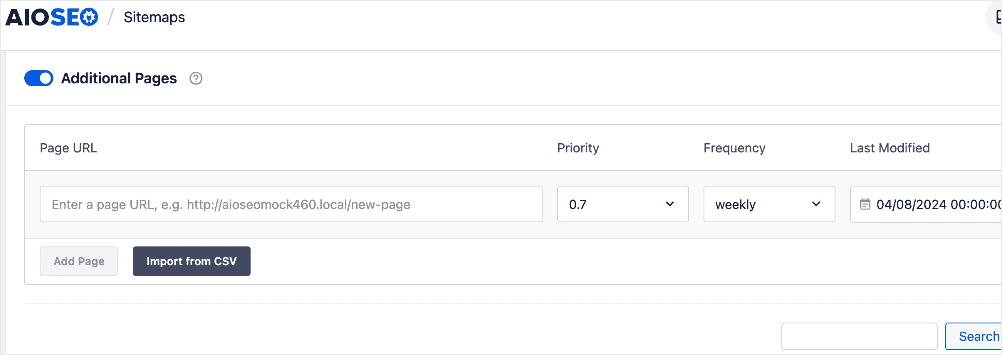
AIOSEO will also automatically notify search engines whenever you publish, update, or delete content on your site.
Check out our tutorial on creating sitemaps in WordPress for step-by-step instructions.
HTML Sitemap vs. XML Sitemap: 5 Main Differences
Now that we’ve looked in-depth at both HTML and XML sitemaps let’s zero in on the main differences between the two.
- Purpose: HTML sitemaps are designed for human visitors, while XML sitemaps are designed for search engines.
- Format: HTML sitemaps are web pages, while XML sitemaps are structured files in the XML format.
- Complexity: HTML sitemaps are generally simpler and easier to create, while XML sitemaps can be more complex and require more technical knowledge.
- Metadata: XML sitemaps can include additional metadata, such as each page’s last modification date and priority, while HTML sitemaps typically do not.
- Submission to search engines: XML sitemaps must be submitted to search engines, while HTML sitemaps don’t require submission.
- Search engine visibility: Search engines primarily use XML sitemaps to understand and crawl your website, while HTML sitemaps are less important for search engine optimization.
While both are sitemaps, HTML and XML sitemaps serve distinct purposes and target different audiences.
Which brings us to the next question…
HTML Sitemap vs. XML Sitemap: Which Should You Use?
In most cases, the best approach is to use both an HTML sitemap and an XML sitemap. The HTML sitemap provides a user-friendly way for visitors to navigate your website, while the XML sitemap helps search engines understand and index your content more effectively.
HTML Sitemap vs. XML Sitemap: Your FAQs Answered
What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that provides a structured list of your website’s pages. An XML sitemap is generated to help search engine bots understand your site’s content and organization better. An HTML sitemap, on the other hand, is for helping your readers better navigate your site.
A sitemap is a file that provides a structured list of your website’s pages. An XML sitemap is generated to help search engine bots understand your site’s content and organization better. An HTML sitemap, on the other hand, is for helping your readers better navigate your site.
Do I need both an HTML and an XML sitemap?
In most cases, using both an HTML and an XML sitemap is recommended. The HTML sitemap is for human visitors, while the XML sitemap is for search engines. Plugins like All In One SEO (AIOSEO) make this easy as they can easily generate both.
In most cases, using both an HTML and an XML sitemap is recommended. The HTML sitemap is for human visitors, while the XML sitemap is for search engines. Plugins like All In One SEO (AIOSEO) make this easy as they can easily generate both.
Do I need to submit my sitemap to search engines?
Submitting your XML sitemap to search engines is recommended, as this can help them crawl and index your website more effectively. You can do this through webmaster tools like Bing Webmaster Tools and Google Search Console (GSC).
HTML sitemaps are less important for search engine submission. However, both contribute to your digital marketing efforts.
What is the difference between HTML and XML sitemaps?
The main difference between HTML and XML sitemaps is that HTML sitemaps are visual and created for your site visitors. XML sitemaps are generated for search engines using a special format called Extensible Markup Language (XML).
The main difference between HTML and XML sitemaps is that HTML sitemaps are visual and created for your site visitors. XML sitemaps are generated for search engines using a special format called Extensible Markup Language (XML).
We hope this post helped you know the difference between HTML sitemaps and XML sitemaps. You may also want to check out other articles on our blog, like our guide to HTML tags and tutorial on setting up automatic redirects.
If you found this article helpful, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel. You’ll find many more helpful tutorials there. You can also follow us on X (Twitter), LinkedIn, or Facebook to stay in the loop.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.