Technical SEO is one of the most fundamental aspects of SEO.
But why is technical SEO important?
Because even the most dazzling content or products won’t shine if hidden from search engines. Understanding and implementing technical SEO is key to staying ahead of your competition.
This guide will help unlock the secrets to search engine rankings and a superior user experience. So, let’s dive in and discover the world of technical SEO together.
1 What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO, a crucial facet of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), encompasses optimizing a website’s technical elements to enhance its visibility and performance in search engine results.
Unlike content or link-based SEO strategies, technical SEO focuses on a website’s structure and functionality.
Key components of technical SEO include website architecture, mobile-friendliness, page speed, and security. Ensuring a clean and crawlable site structure, employing SEO-friendly URLs, and implementing proper header tags are integral to technical SEO.
In essence, technical SEO ensures that search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and rank a website, improving its online presence and user experience. Businesses can lay a robust foundation for a successful SEO strategy by addressing these technical aspects.
2 Why is Technical SEO Important?
Technical SEO is important because it helps search engines understand and index your website correctly. This is essential for ranking well in SERPs and driving organic traffic to your site.
We’ve listed a few benefits of technical SEO.
- Improved website performance: Technical SEO can help improve your website’s loading speed, a key ranking factor. A faster website is also more user-friendly, which can lead to lower bounce rates and higher conversion rates.
- Increased organic traffic: When your website is technically sound, search engines are more likely to crawl and index it properly. This means your pages are more likely to appear in SERPs for relevant keywords, which can significantly increase organic traffic.
- Better user experience: A technically sound website is also more user-friendly. This means visitors are more likely to stay on your site longer and explore more pages.
- Improved security: Technical SEO can also help to improve your website’s security. By fixing vulnerabilities and implementing security best practices, you can reduce the risk of your website being hacked or compromised.
Overall, technical SEO is an essential part of any SEO strategy. By optimizing the technical aspects of your website, you can improve its performance, visibility, and user experience.
If you’re serious about improving your website’s SEO, investing in technical SEO is important.
3 Best Practices for Technical SEO
We’ll now discuss the best practices you can follow to improve your technical SEO.
3.1 Website Structure
A well-optimized website structure is the backbone of effective technical SEO, ensuring search engines can crawl and index content effortlessly. Intuitive navigation, complemented by clear hierarchies, enhances user experience and improves search engine rankings.
URL Structure
URL structure is a cornerstone of effective technical SEO, contributing significantly to a website’s visibility in search engine results.
Your URLs should be user-friendly, consistent, easily understandable, and optimized for search engines. Characteristics of SEO-friendly URLs include the use of relevant keywords, clear structure, and the avoidance of unnecessary parameters or symbols.
By creating URLs that align with the content they represent, websites enhance the user experience and make it easier for search engines to interpret and index the pages.
Canonicalization
Canonicalization is a key aspect of technical SEO that addresses the issue of duplicate content. Various URLs can sometimes lead to identical or similar content, causing confusion for search engines.
Canonicalization involves using canonical tags to designate the preferred version of a URL, consolidating the ranking signals for that specific content.
This practice helps search engines understand the primary source of content and avoid indexing multiple versions of the same page.
By implementing canonicalization, websites can mitigate the risk of diluting SEO value due to duplicate content, ensuring more accurate indexing and ranking in search engine results.
You can easily change the canonical URLs in Rank Math. You can further refer to our detailed guide on canonical URLs.
3.2 Indexability and Crawling
In technical SEO, indexability and crawling are important in determining how search engines navigate and index a website’s content.
Using a robots.txt file is a key practice, serving as a set of instructions for web crawlers on which pages or sections to exclude from crawling or indexing.
On the other hand, XML sitemaps provide a structured roadmap for search engines, listing URLs and additional information about the website’s content, which we’ll cover in detail in the next segment.
This aids in efficient crawling and ensures that search engines can discover and index all relevant pages, especially useful for large or complex websites.
Additionally, the handling of directives such as noindex, nofollow, and disallow plays a vital role in controlling the behavior of search engine bots.
The noindex directive is used to prevent the indexing of specific pages, while nofollow is applied to links, guiding search engines not to follow or crawl the linked pages. Meanwhile, the disallow directive in robots.txt restricts the crawling of particular sections, enhancing the webmaster’s control over the indexing process.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on editing the robots.txt file in Rank Math.
3.3 XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps enhance a site’s visibility and performance in search engine results by creating and submitting them to the search engines.
Creating XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps serve as crucial navigational guides for search engines, offering a roadmap to the various pages of a website.
Creating XML sitemaps involves generating a file that lists the URLs of a site along with additional metadata about each URL, such as the date of last modification and the frequency of changes.
This helps search engine crawlers understand the site’s structure, ensuring comprehensive indexing. XML sitemaps are particularly beneficial for large websites with intricate structures or pages that may not be easily discoverable through conventional crawling methods.
Rank Math generates search engine-compatible XML Sitemaps for your website automatically.
Submitting Sitemaps to Search Engines
Once XML sitemaps are created, the next step in the technical SEO process is submitting them to search engines.
This involves notifying search engine giants, such as Google and Bing, about the existence of the XML sitemap and its location. Search engines can then use this information to crawl and index the site’s pages efficiently.
The submission process varies among search engines but often involves utilizing their respective webmaster tools or search console platforms.
Regularly updating and resubmitting XML sitemaps is recommended, especially after significant changes to the website, to ensure search engines are aware of the latest content and structural updates.
After your sitemaps are submitted, Rank Math will automatically update any new content you add to your website to the respective sitemaps, and Google will be able to fetch that content seamlessly.
You can further refer to our detailed guide that’ll help you configure sitemaps in Rank Math seamlessly.
3.4 Site Navigation
Site navigation is a critical component of technical SEO, influencing how search engines and users navigate and understand a website’s content. Effective site navigation ensures that both search engines and users can easily access and comprehend the structure of a site.
Websites can enhance their technical SEO by implementing a clear hierarchical structure and breadcrumbs, improving search engine rankings and user satisfaction.
Clear Hierarchical Structure
Establishing a clear hierarchical structure is essential for technical SEO. This involves organizing website content logically and hierarchically, clearly distinguishing between main categories and subcategories.
For instance, an e-commerce site might have a top-level category for “Electronics” with subcategories like “Mobiles” and “Cameras.” This hierarchical structure helps search engines comprehend the relationships between different pages, enhancing the site’s overall visibility.
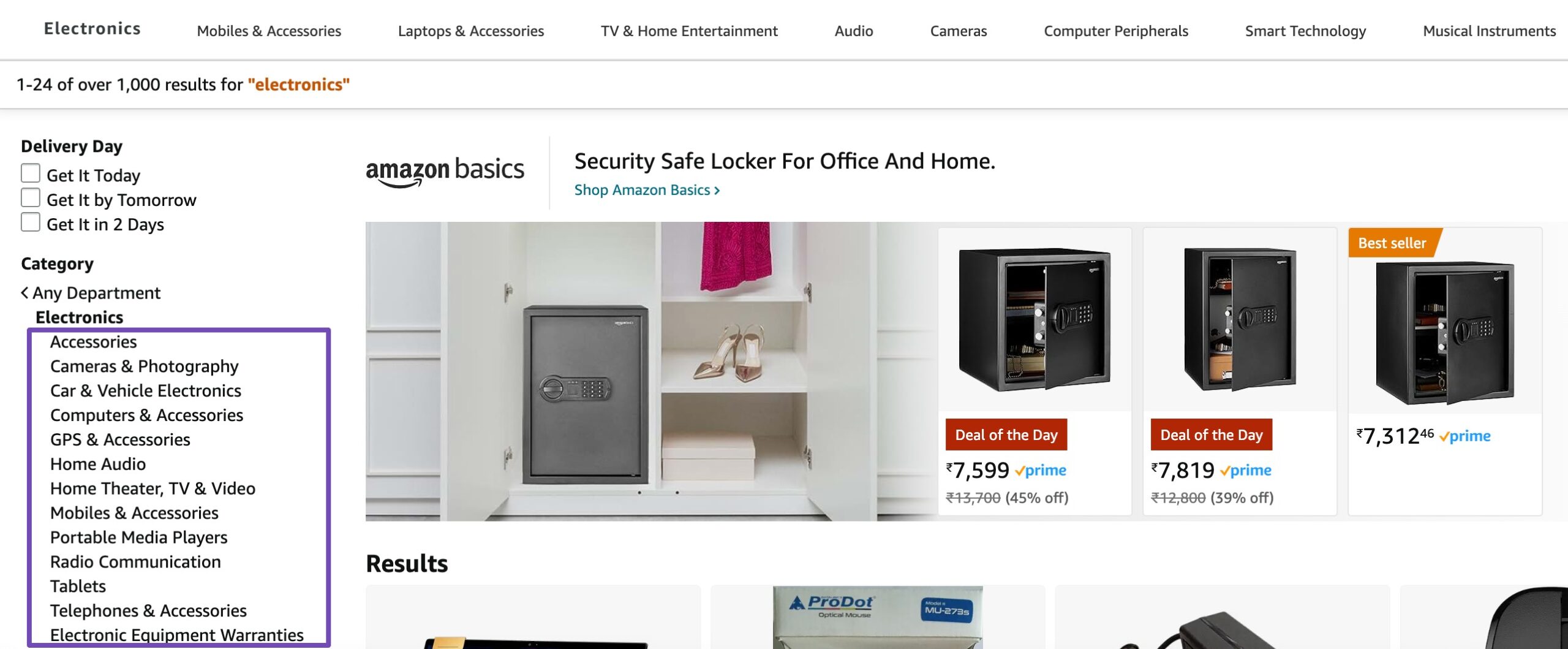
Clear hierarchies also make it easier for users to navigate, improving the user experience.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs provides a navigational trail, displaying the user’s path from the homepage to the current page. From a technical SEO perspective, breadcrumbs offer contextual information to search engines, aiding in better understanding the website’s structure.
Rank Math SEO plugin simplifies adding the Breadcrumb Schema, a requirement for search engines to display breadcrumbs in search results. For example, here’s how we use breadcrumbs on our page.

This can lead to improved indexing and potentially enhanced visibility in search results. Moreover, breadcrumbs contribute to a positive user experience by offering a simple and intuitive way for users to retrace their steps within the site.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on enabling breadcrumbs in Rank Math.
3.5 Use Structured Data
Structured data helps Google comprehend a page’s content more effectively.
By incorporating the appropriate Structured data markup code, your pages have the potential to secure rich snippets. Rich snippets transform search results into more captivating displays, including supplementary information beneath the title and description, as shown below.
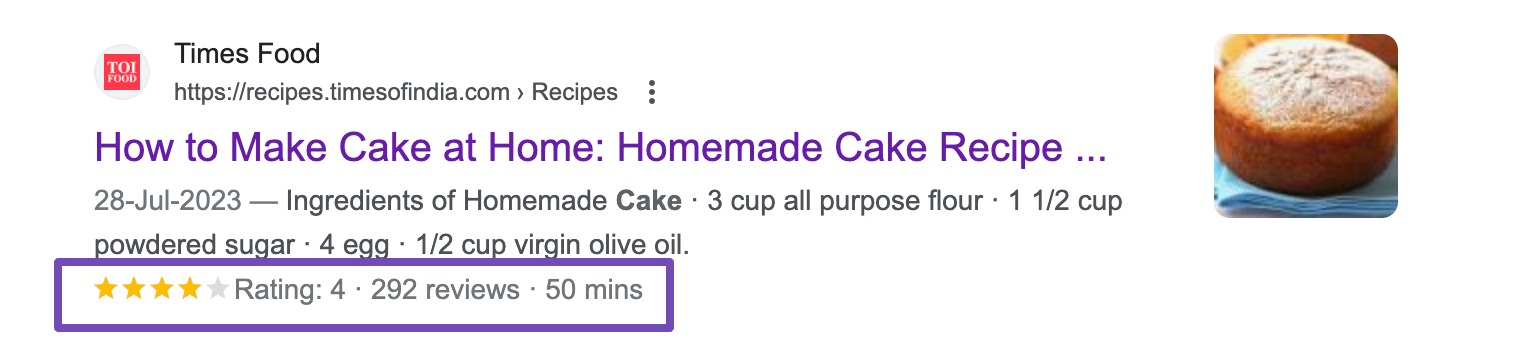
Adding Structured data to your posts with Rank Math is as easy as a point-and-click process. Rank Math supports various Schema types, and you can also set a default category in the settings.
3.6 Mobile Optimization
Mobile optimization is a pivotal aspect of website development, ensuring an enhanced user experience for visitors accessing a site from mobile devices.
Mobile User Experience
The mobile user experience encompasses navigation, readability, and functionality. A seamless and intuitive mobile experience contributes to higher user satisfaction and engagement.
Elements such as easily tappable buttons, legible fonts, and simplified navigation menus all play a role in creating a positive mobile user experience.
Google values user experience and considers it when determining search rankings. Utilize the Mobile Usability report in Google Search Console. If Google identifies that a page on your site isn’t optimized for mobile users, they’ll promptly notify you.
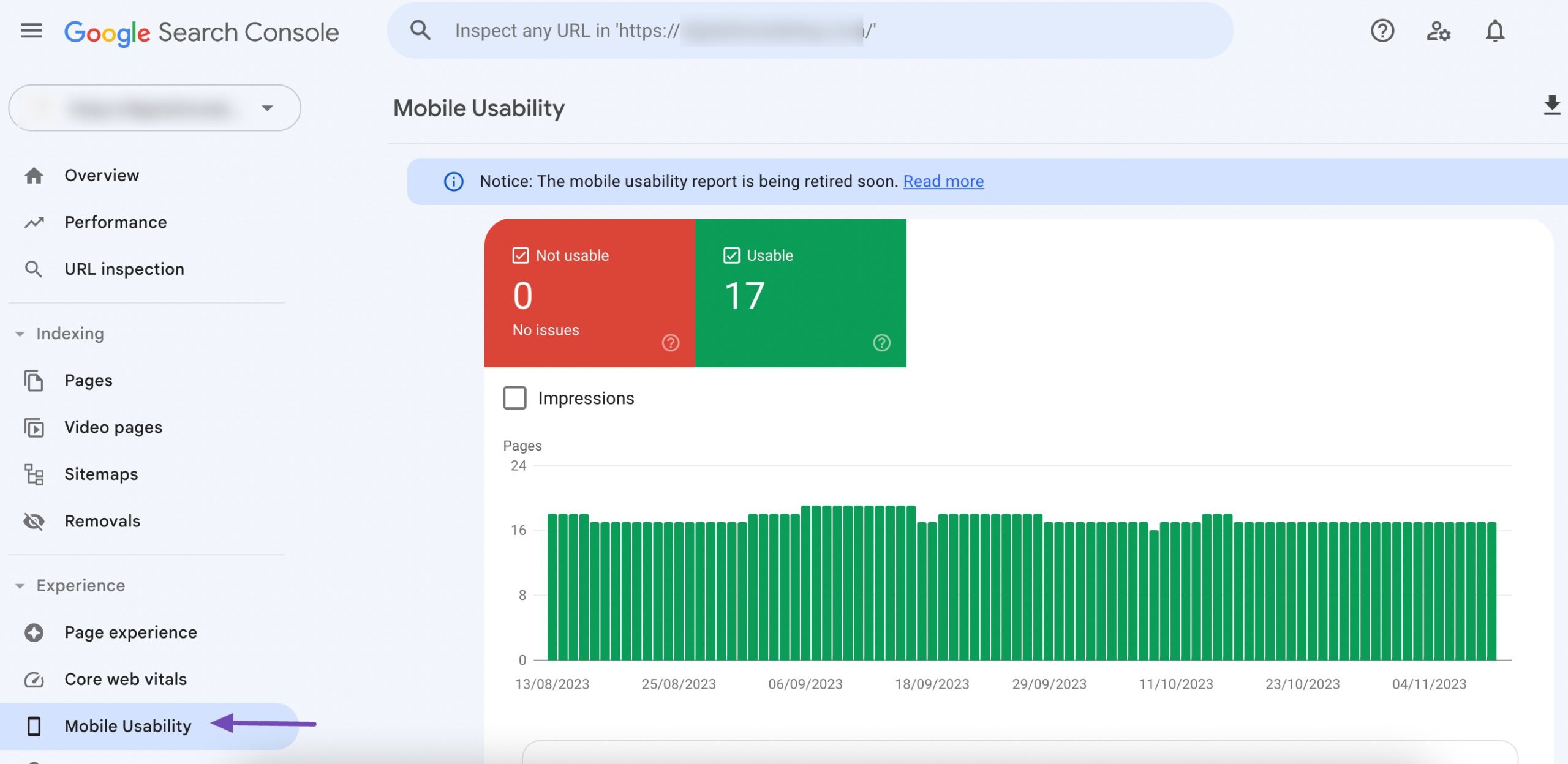
Mobile-Friendly Navigation
Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings, and having a navigation system optimized for smaller screens is imperative.
Responsive design, where the layout adapts to different screen sizes, is a common approach. For example, a mobile-friendly navigation menu might use a collapsible menu to conserve screen space. This meets Google’s mobile-friendliness criteria and enhances the user experience on mobile devices, contributing to improved SEO performance.
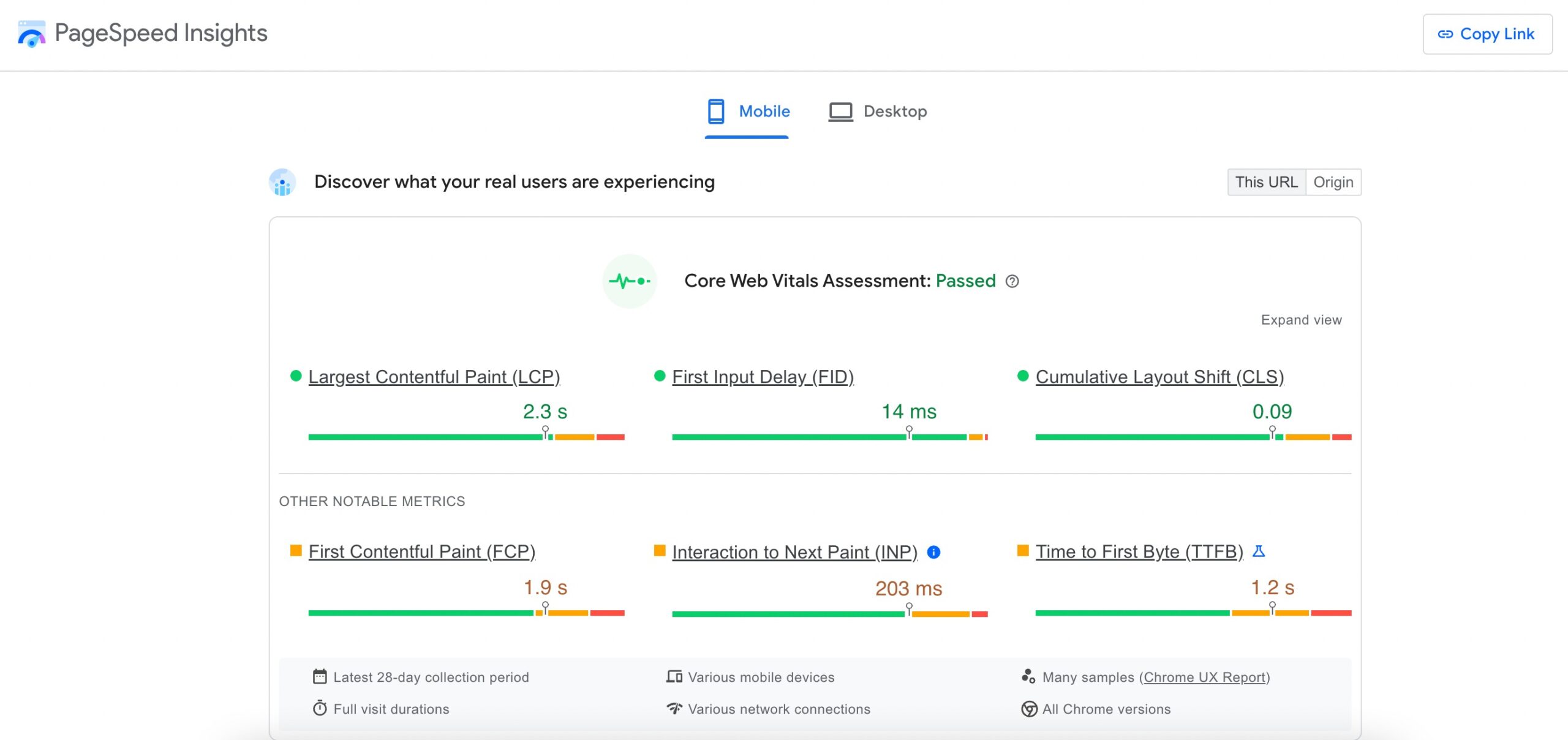
Mobile Page Speed
Mobile page speed is a critical factor influencing user experience and search rankings. Mobile users often expect quick loading times, and Google considers page speed in its ranking algorithms on mobiles and desktops.
Optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and minimizing server requests are common strategies to enhance mobile page speed.
Ensuring swift load times not only pleases users but also aligns with Google’s preferences. Use PageSpeed Insights to check where your website needs to improve.
3.7 Find and Remove Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to identical or substantially similar content that appears in more than one place, either on the same website or across different websites.
Causes of duplicate content can stem from various sources, including URL variations (http vs. https, trailing slashes), printer-friendly versions, session IDs, and content syndication.
Content management system (CMS) issues, URL parameters, and e-commerce platforms may inadvertently generate duplicate content.
How to Identify Duplicate Content
Identifying duplicate content is crucial for effective technical SEO. You can use tools like Semrush’s Site Audit tool to detect duplicate content issues.
Additionally, manual checks, such as searching for excerpts of content within quotation marks on search engines, can help uncover instances of duplicate content.
Regularly monitoring website analytics and conducting content audits are proactive measures to identify and address duplicate content before it adversely affects SEO performance.
Strategies to Handle Duplicate Content
Addressing duplicate content requires strategic implementation:
- Canonicalization: As explained before, use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page when duplicate content exists. This informs search engines about the primary source and consolidates ranking signals.
- 301 Redirects: Implementing 301 redirects from duplicate URLs to the canonical version helps consolidate link equity and ensures that users and search engines are directed to the correct page.
- Parameter Handling: Configure URL parameters in Google Search Console to guide search engines on how to treat variations. This is particularly relevant for e-commerce sites with filtering options.
- Content Syndication Best Practices: If syndicating content, use rel=”canonical” tags to prevent duplicate content issues. Ensure that syndicated content adds value and includes proper attribution.
- Consistent Internal Linking: Maintain a consistent internal linking structure to avoid unintentional creation of duplicate content through multiple pathways.
3.8 Page Speed Optimization
Page speed significantly influences user experience. Faster-loading pages lead to lower bounce rates and increased user satisfaction.

Compress images without compromising quality using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim.
Minify CSS and JavaScript files by removing unnecessary spaces, line breaks, and comments. Enable browser caching to store static resources locally on a user’s device.
Set appropriate expiration headers for cached resources to ensure users receive the latest content when necessary.
You can use the best caching plugin, like WP-Rocket, to speed up your website’s pages and result in faster load times.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on Page Speed Optimization to deliver exceptional performance to your audience.
3.9 Ensure Website Security
Prioritizing website security in technical SEO is necessary for user trust and search engine rankings.
SSL Certificates and HTTPS
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates are fundamental for website security. They encrypt the data between a user’s browser and the website’s server, preventing unauthorized access. An SSL certificate is crucial for security and positively influences search engine rankings.
Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) ensures a secure and encrypted connection.
Protection Against Malware and Hacking
Utilize firewalls and security plugins to fortify your website against hacking attempts and malware. These tools actively monitor and filter out malicious traffic, enhancing overall security.
Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities. Addressing potential weaknesses promptly helps prevent unauthorized access and protects sensitive data.
Regular Backups
Regularly back up your website’s data and files. This ensures that you can quickly restore your site to a previous, secure state in case of a security breach or data loss.
Store backups in secure, off-site locations to safeguard against server failures or other disasters that could compromise your primary data storage.
Data Privacy and GDPR Compliance
Prioritize the protection of user data. Ensure that sensitive information is encrypted and stored securely, adhering to best practices for data privacy.
Comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) standards, especially if your website collects or processes data from users in the European Union. This involves obtaining explicit consent for data collection and implementing measures to secure and manage user data responsibly.
4 Wrapping It Up
Mastering technical SEO is a must for online success. From optimizing page speed to securing your website, this guide has revealed the techniques that define a robust technical SEO strategy.
As you refine your website’s architecture, implement these insights, leverage cutting-edge tools, and stay informed of evolving algorithms.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.

